 A capacitor or condenser is an electrical or electronic device that can store energy. A capacitor or condenser is an electrical or electronic device that can store energy.
It stores the energy within the electric field between a pair of conductors (called "plates"). The process of storing energy in the capacitor is known as "charging", and involves electric charges of equal size, but opposite charge, building up on each plate.
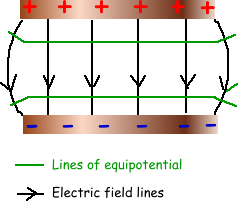 Once charged the plates have a uniform electric field between them. Within the main body of the plates this field is truly uniform - but at the edges the uniformity is disrupted due to 'edge effects'. Therefore any practical work should take account of this. Once charged the plates have a uniform electric field between them. Within the main body of the plates this field is truly uniform - but at the edges the uniformity is disrupted due to 'edge effects'. Therefore any practical work should take account of this.
Capacitors are often used in electric and electronic circuits as energy-storage devices. There are many different types but in physics questions you are usually asked about a simple parallel plate capacitor. In electronics you will learn about the many types and their uses. |


