Capacitance
The capacitor's capacitance (C) is a measure of the quantity of charge (Q) stored on each plate when a given potential difference or voltage (V) is applied across the plates:
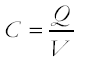
So capacitance is defined as:
The ratio of charge stored on an isolated conductor to the difference in potential.
Or
The charge required to cause unit potential difference in a conductor
Units
In SI units, a capacitor has a capacitance of one farad (F) when one coulomb (C) of charge is stored when one volt (V) of potential difference is applied across the plates.
Since the farad is a very large unit, values of capacitors are usually expressed in microfarads (µ F), nanofarads (nF), or picofarads (pF).
 |
Ready for some questions?
Click on the graphic - Multiple Choice questions and answers at A level standard await you!
For more topics that have practice questions associated with them see the upper left menu bar
|
 |
Ready for some questions?
Click on the graphic - Short Response questions and answers at A level standard await you!
For more topics that have practice questions associated with them see the upper left menu bar
|
