3.3.1.1
Progressive Waves |
Oscillation of the particles of the medium;
amplitude,
frequency,
wavelength,
speed,
phase,
path difference.
|
Progressive waves transport energy from one place to another.
Phase difference may be measured as angles (radians and degrees) or as fractions of a cycle. |
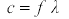
T = 1/f
PS 2.3 / MS 0.1, 4.7 / AT a, b Laboratory experiment to determine the speed of sound in free air using direct timing or standing waves with a graphical analysis. |
3.3.1.2
Longitudinal and transverse waves |
Nature of longitudinal and transverse waves.
Characteristics and examples, including sound, electromagnetic
waves and waves on a string.
|
Polarisation as evidence for the
nature of transverse waves; applications e.g.
Polaroid sunglasses, aerial alignment for transmitter and
receiver. |
PS 2.2, 2.4 / MS 1.2, 3.2, 3.4, 3.5 / AT i Students can investigate the factors that determine the speed of a water wave. |
|
Students will be expected to know:
- the direction of displacement of particles/fields relative to the direction of energy propagation and that
- all electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed in a vacuum. |
|
|
| Polarisation as evidence for the nature of transverse waves. |
Applications of polarisers to include Polaroid material and the alignment of aerials for transmission and reception. |
Malus's law will not be expected. |
|
| 3.3.1.3 Superposition of waves and formation of Stationary waves |
The formation of stationary waves by two waves of the same frequency travelling in
opposite directions;
Nodes and antinodes on strings.
|
A graphical explanation of formation of stationary waves will be expected. Stationary waves formed on a string and those produced with microwaves and sound waves should be considered. Stationary waves on strings will be described in terms of harmonics.
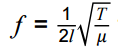
for the first harmonic
The terms fundamental (for first harmonic) and overtone will not be used.
|
MS 4.7 / PS 1.2, 2.1 / AT i Students can investigate the factors that determine the frequency of stationary wave patterns of a stretched string.
Required practical 1: Investigation into the variation of the frequency of stationary waves on a string with length, tension and mass per unit length of the string. |


