Academic Applications - Uses of Nuclear Radiation The most common and accepted method of 'absolute geologic dating' (establishment of actual age) is based on the natural radioactivity of certain minerals found in rocks. As the rate of radioactive decay of any particular isotope is known, the age of a specimen can be worked out from the ratio of the remaining isotope and its decay product.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Initial Value |
100.00%
|
0.00%
|
|
0
|
| After one half-life |
50.00%
|
50.00%
|
|
4,500
|
| After two half-lives |
25.00%
|
75.00%
|
|
9,000
|
| After three half-lives |
12.50%
|
87.50%
|
|
13,500
|
| After four half-lives |
6.25%
|
93.75%
|
|
18,000
|
 Dating
of Ancient Artefacts (Carbon Dating)
Dating
of Ancient Artefacts (Carbon Dating)
Carbon dating measures the remaining amount of the radioactive isotope carbon-14 in organic matter. It can be used to date specimens as old as 35,000 years.
During its lifetime a biological entity (plant or animal) takes an active part in the carbon cycle and it contains the same proportion of the isotope as the atmosphere does (about one ten millionth of the carbon is carbon-14).
The death of an organism terminates the incorporation of this isotope into the fabric of the entity. From the time of death onwards the proportion of carbon-14 in the dead orgamism decreases as it decays into nitrogen.
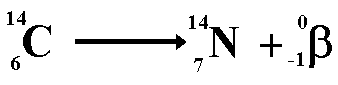
By calculating the ratio of C-14 to total carbon in a sample of the artefact it is possible to work out its age. The half-life of carbon-14 is 5,600 years.
E.g.
| C-14 in total carbon |
Age
(years)
|
|
| Initial Value | 1 part in 10 million |
0
|
| After one half-life | 0.5 parts in 10 million |
5,600
|
| After two half-lives | 0.25 parts in 10 million |
11,200
|
| After three half-lives | 0.125 parts in 10 million |
16,800
|
| After four half-lives | 0.0625 parts in 10 million |
22,400
|
Follow me...





