6.3.1
|
(a) magnetic fields are due to moving charges or permanent magnets |

|
| (b) magnetic field lines to map magnetic fields |
(c) magnetic field patterns for a long straight current-carrying conductor, a flat coil and a long solenoid |
(d) Fleming's left-hand rule |
(e) (i) force on a current-carrying conductor;
F = BI L sin θ |
(e) (ii) techniques and procedures used to determine the uniform magnetic flux density between the poles of a magnet using a current-carrying wire and digital balance |
| (f) magnetic flux density; the unit tesla. |
6.3.2 Motion of charged particles |
(a) force on a charged particle travelling at right angles to a uniform magnetic field;
F = BQv |
|
|
| (b) charged particles moving in a uniform magnetic field;
circular orbits of charged particles in a uniform magnetic field |
|
Learners will also require knowledge of 3.2, 3.3 and 5.2 |
(c) charged particles moving in a region occupied by both electric and magnetic fields; velocity selector. |
|
|
6.3.3
Electromagnetism |
(a) magnetic flux φ;
the unit weber;
φ = BAcosθ |
|
|
| (b) magnetic flux linkage |
|
|
(c) Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction and Lenz's law |
|
|
(d) (i) e.m.f. = − rate of change of magnetic flux linkage;
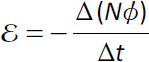
|
|
|
(d) (ii) techniques and procedures used to investigate magnetic flux using search coils |
|
|
| (e) simple a.c. generator |
|
|
(f) (i) simple laminated iron-cored transformer;
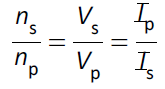
for an ideal transformer |
|
|
| (f) (ii) techniques and procedure |
|
|


