6.1.1
|
(a) capacitance;
C = Q/V
the unit of the farad |

|
(b) charging and discharging of a capacitor or capacitor plates with reference to the flow of electrons. |
(c) total capacitance of two or more capacitors in series;
1/C = 1/C1 + 1/C2 + .... |
(d) total capacitance of two or more capacitors in parallel;
C = C1 + C2 + ... |
(e) (i) analysis of circuits containing capacitors, including resistors |
(e) (ii) techniques and procedures used to investigate capacitors in both series and parallel combinations using ammeters and voltmeters. |
6.1.2
Energy |
(a) p.d. – charge graph for a capacitor; energy stored is area under graph |
|
|
(b) energy stored by capacitor;
W = ½QV
W = ½ (Q2/C)
W = ½ (V2/C) |
|
|
| (c) uses of capacitors as storage of energy. |
|
|
6.1.3
Charging and discharging capacitors |
(a) (i) charging and discharging capacitor through a resistor |
|
|
(ii) techniques and procedures to investigate the charge and the discharge of a capacitor using both meters and data-loggers |
|
Investigating the charge and discharge of capacitors in the laboratory. |
(b) time constant (tau) of a capacitor–resistor circuit;
τ = CR |
|
|
(c) equations of the form
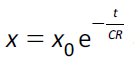
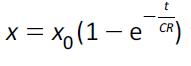
for capacitor–resistor circuits |
|
Learners will be expected to know how ln x–t graphs can be used to determine CR |
(d) graphical methods and spreadsheet modelling of the equation
ΔQ/ΔT = - Q/CR
for a discharging capacitor |
|
Using spreadsheets to model the discharge of a capacitor. |
(e) exponential decay graph;
constant-ratio property of such a graph. |
|
|


