3.4.2.1 Bulk properties of solids
|
Density |
|
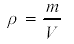 |
| Stretching solids |
Hooke's law |
elastic limit,
investigations. |
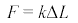 k as stiffness and spring constant. k as stiffness and spring constant. |
| |
Tensile strain and tensile stress.
Elastic strain energy
Breaking stress.
|
Derivation of stored energy
Description of plastic behaviour, fracture and brittleness linked to force–extension graphs.
|
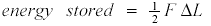
= area under force−extension graph
|
|
Interpretation of simple stress-strain curves. |
Appreciation of energy conservation issues in the context of ethical transport design. |
Quantitative and qualitative application of energy conservation to examples involving elastic strain energy and energy to deform.
Spring energy transformed to kinetic and gravitational potential energy.
|
| 3.4.2.2 The Young Modulus |
Use of stress-strain graphs to find the Young modulus. |
One simple method of measurement.
|
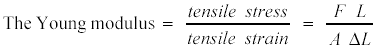
Required practical 4: Determination of the Young modulus by a simple method. |


