Waves - Multiple Choice Questions Q1. Two points on a progressive wave are one-eighth of a wavelength apart. The distance between them is 0.5 m, and the frequency of the oscillation is 10 Hz. What is the minimum speed of the wave?
λ = 8 x 0.5m = 4.0 m c = fλ c = 4.0 x 10 = 40 m s−1 Q2. Which of the following waves cannot be polarised?
Sound waves are longitudinal and cannot be polarised the others are transverse electromagnetic waves. Q3. Which of the following is correct for a stationary wave?
Q4. Sound waves cross a boundary between two media X and Y. The frequency of the waves in X is 400Hz. The speed of the waves in X is 330 ms −1 and the speed of the waves in Y is 1320 ms –1 . What are the correct frequency and wavelength in Y?
Frequency does not change when the wave passes into another medium. c = fλ λ =c/f λ = 1320 /400 = 3.3 m Q5. What is the phase difference between two points 0.16 m apart on a progressive sound wave of frequency 256 Hz? speed of sound = 330 m s–1
speed = fλ λ = 330/256 λ = 1.29 m 0.16/1.29 = 0.124 ≈ 1/8th 2π/8 = π/4
Q6. The frequency of the first harmonic of a standing wave on a wire is f. The length of the wire and tension in the wire are both doubled. What is the frequency of the first harmonic as a result?
doubling the length halves the frequency doubling the tension increases it by √2
overall effect = √2/2
but 2 = √2 x √2 so, overall effect = √2/(√2√2)
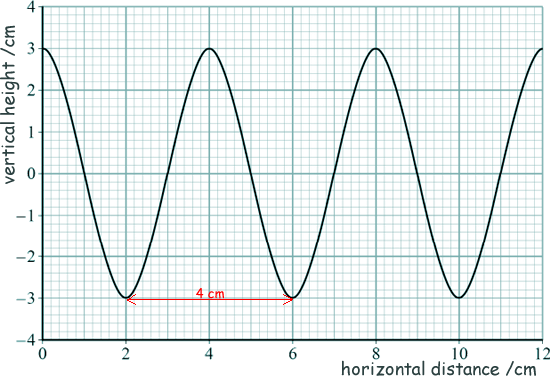
= 1/√2 Choice A Q7. The graph below shows how the vertical height of a travelling wave varies with distance along the path of the wave.
The speed of the wave is 20 cm s–1. What is the period of the wave? wavelength λ = 4 cm (see graph) speed v = fλ f = v/λ f = 20/4 = 5 Hz T = 1/f T = 1/5 = 0.2 s Choice B
Q8. Which statement is not correct for ultrasound and X-rays?
Q9. A stationary wave is set up on a stretched string of length l and diameter d. Another stationary wave is also set up on a second string made from the same material and with the same tension as the first. What length and diameter are required for the second string so that both strings have the same first-harmonic frequency?
linear density μ = m/L Volume V = L x ¼πd2 density ρ = m/V so, ρ = m/(Lπd2) and, m = ρLπd2 Substituting into μ = m/L we get: μ = ρLπd2/L = ρπd2 ∴ f ∝ 1/L and as f ∝ √μ but μ∝ d2 f ∝ d So if diameter doubles length must halve - choice C
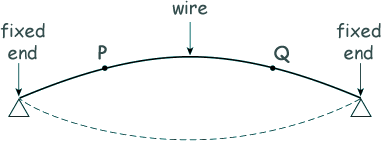
Q10. A uniform wire, fixed at both ends, is plucked in the middle so that it vibrates at the first harmonic as shown.
What is the phase difference between the oscillations of the particles at P and Q?
Q11. Which row correctly shows electromagnetic radiations in order of decreasing wavelength?
decreasing wavelength - biggest wavelength first - so microwave as starter
Q12. Which statement is correct about the properties of an unpolarised electromagnetic wave as it passes through a polariser?
|
Follow me...
|