'A' Level Medical Option Questions - The Heart - ECG
Q1.
The graph below shows a normal electrocardiogram (ECG) signal obtained at the surface of the skin of a patient.
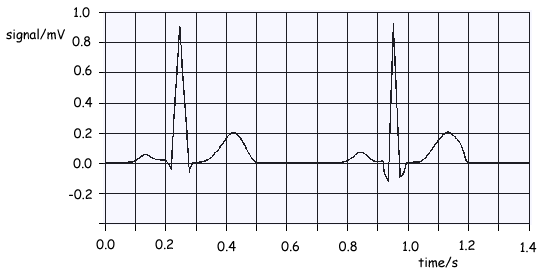
(a) What is the amplitude of the main pulse in the signal?
1 mark
(b) Find the period of the heart beat and from it calculate the pulse rate per minute.
2 marks
(c) What changes would you expect to see in the electrocardiogram if the patient began to take exercise?
2 marks
(d) On the graph, label with a P the points where atrial contraction occurs and with a Q the points where ventricular contraction starts.
2 marks
Total 7 marks

Q2. Electrodes are attached to the chest of a healthy person and a normal ECG waveform is obtained.
(a) State two ways of ensuring good electrical contact between the electrodes and the person.
2 marks
(b) State two properties of the amplifier needed to amplify the signal from the electrodes.
2 marks
(c) Sketch, on the axes below, the waveform that you would expect to obtain. Label the axes with appropriate scales.
Mark on the waveform where the following occur:
(i) atrial depolarisation
(ii) ventricular depolarisation
(iii) ventricular repolarisation.
5 marks
Total 9 marks

Q3. The graph below shows the variation of membrane potential difference with time of a nerve fibre, known as an action potential.
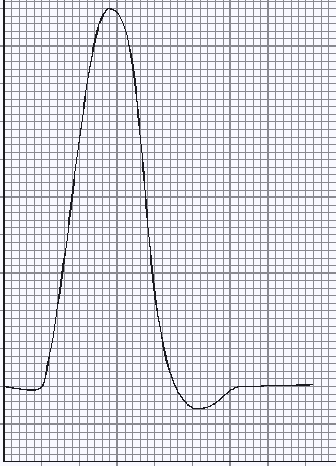
(a) Complete the graph by adding suitable axes, units and scales.
3 marks
(b) Describe the processes involved in the production of such an action potential when a nerve is stimulated.
3 marks
Total 6 marks

Q4.
(a) Describe the response of the heart to the action potential originating at the sino-atrial node.
4 marks
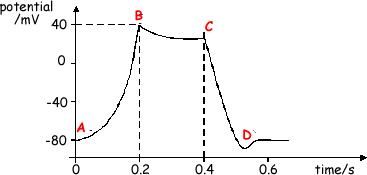
(b) The cell membrane action potential changes with time as shown. The change in action potential results from ion movement in the same way as does the change of action potential across a nerve membrane. AB is a region of depolarisation. CD is a region of repolarisation.
(i) Describe the ion movement which produces depolarisation.
(ii) Describe the ion movement which produces repolarisation.
3 marks
Total 7 marks

Q5. Electrodes are placed on the surface of a body to record an ECG trace for a healthy person. The trace obtained for one heartbeat is shown below.
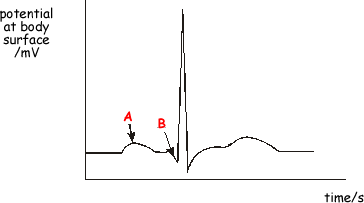
(a)
(i) Label approximate scales on each axis.
(ii) State what electrical event happens at points A and B and the physical change that results.
6 marks
(b) State, giving a reason, one precaution you would take when attaching the electrodes to the surface of the skin to ensure a good signal is obtained.
2 marks
(c) The amplifier used must have a high gain. State two other properties of the amplifier.
2 marks
Total 10 marks

Q6.
(a) Sketch a graph of the ECG trace for a healthy heart. Label each axis with appropriate units and scales.
4 marks
(b) When obtaining such a trace, electrodes are attached to the patient. State and explain two precautions which should be taken when attaching the electrodes to ensure reception of the best signal.
2 marks
Total 6 marks

Q7.
(a) The diagram shows the ECG waveform produced when electrodes are attached to the chest of a healthy person. Label the axes with suitable scales and units.
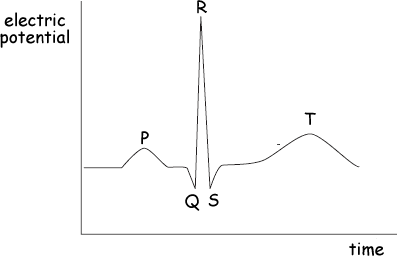
(2 marks)
(b) State what is meant by depolarisation and repolarisation and, in terms of ion movement, explain how each effect is caused.
(3 marks)
(c) State how the action of the atria and ventricles correspond to the waveform PQRST shown in the diagram
(3 marks)
(Total 8 marks)

Q8.
(a) An ECG trace is to be obtained for a patient. State and explain the procedure and some design features of the equipment needed to ensure a good trace is obtained.
(6 marks)
(b) The diagram below shows an ECG trace for a healthy person.
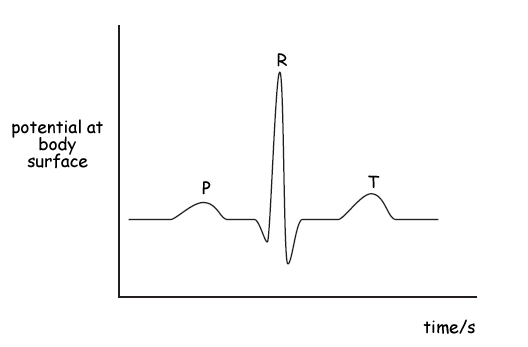
(i) Add a suitable scale and unit to the potential axis.
(2 marks)
(ii) Add a suitable scale to the time axis.
(1 mark)
(iii) State the electrical events which give rise to the points P, R amd T.
(3 marks)
(Total 12 marks)















