Gravitational fields - Multiple Choice Q11. When at the surface of the Earth, a satellite has weight W and gravitational potential energy U. It is projected into a circular orbit whose radius is equal to twice the radius of the Earth. Which line, A to D, in the table shows correctly what happens to the weight of the satellite and to its gravitational potential energy?
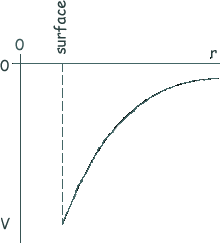
Q12. The sketch graph shows how the gravitational potential, V, varies with the distance, r , from the centre of the Earth.
What does the gradient of the graph at any point represent?
Q13. Near the surface of a planet the gravitational field strength is uniform and for two points, 10 m apart vertically, the gravitational potential difference is 3 J kg–1. How much work must be done in raising a mass of 4 kg vertically through 5 m?
Q14. What would the period of rotation of the Earth need to be if objects at the equator were to appear weightless?
Q15. The Earth has density ρ and radius R. The gravitational field strength at the surface is g. What is the gravitational field strength at the surface of a planet of density 2ρ and radius 2R?
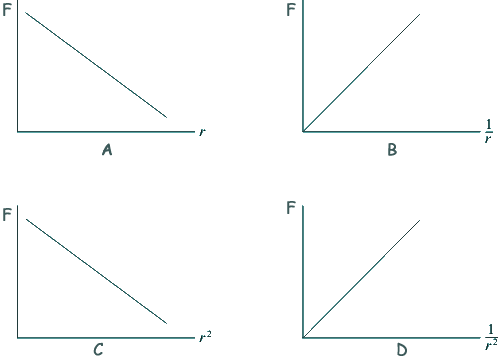
Q16. Which one of the following graphs correctly shows the relationship between the gravitational force, F, between two masses and their separation r?
Q17. Which one of the following could be a unit of gravitational potential?
Q18. The radius of a certain planet is x times the radius of the Earth and its surface gravitational field strength is y times that of the Earth. Which one of the following gives the ratio
Q19. A planet of mass M and radius R rotates so rapidly that loose material at the equator only just remains on the surface. What is the period of rotation of the planet?
Q20. As a comet orbits the Sun the distance between the comet and the Sun continually changes. As the comet moves towards the Sun this distance reaches a minimum value. Which one of the following statements is incorrect as the comet approaches this minimum distance?
|
Follow me...
|