Circuits - series and parallel
Q6. X and Y are two lamps. X is rated at 12V 36W and Y at 4.5V 2.0W.
(a) Calculate the current in each lamp when it is operated at its correct working voltage.
P = IV
I = P/V
I (lamp X) = 36/12 = 3.0A 
I (lamp Y) = 2.0/4.5 = 0.44A 
(2 marks)
(b) The two lamps are connected into the circuit as shown in the diagram below.
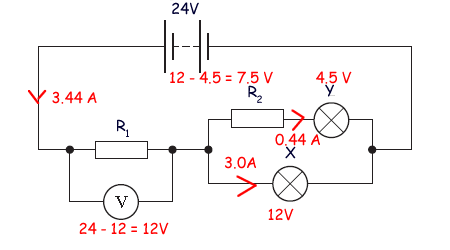
(i) Calculate the pd across R1. 24 - 12 = 12V 
(ii) Calculate the current in R1. current = 3.0 + 0.44 = 3.44A 
(iii) Calculate the resistance of R1. V = IR so R = V/I = 12/3.44 = 3.5 Ω 
(iv) Calculate the pd across R2. 12 - 4.5 = 7.5 V 
(v) Calculate the resistance of R2. V = IR so R = V/I = 7.5/0.44 = 17 Ω 
(5 marks)
(c) The filament of the lamp in X breaks and the lamp no longer conducts. It is observed that the voltmeter reading decreases and lamp Y glows more brightly.
(i) Explain without calculation why the voltmeter reading decreases.
When the bulb blows the resistance of the parallel section increases  therefore it takes a bigger share of the [ptential difference provided by the battery
therefore it takes a bigger share of the [ptential difference provided by the battery  and the voltage across resistor 1 will decrease, making the voltmeter reading drop.
and the voltage across resistor 1 will decrease, making the voltmeter reading drop.
OR the resistance of the complete circuit increases,  thus the current through resistor 1 will decrease, and as R = V/I so will the potential difference across it.
thus the current through resistor 1 will decrease, and as R = V/I so will the potential difference across it.
(2 marks max)
(ii) Explain without calculation why the lamp Y glows more brightly.
The pd across Y (or current through Y) increases  hence the power (rate of energy dissipation) will be greater
hence the power (rate of energy dissipation) will be greater making the temperature of the lamp increase
making the temperature of the lamp increase
(2 marks max)
(Total 11 marks)



