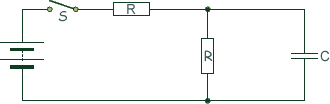
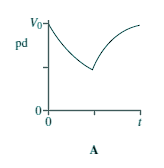
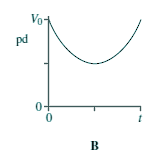
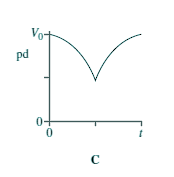
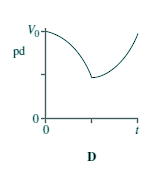
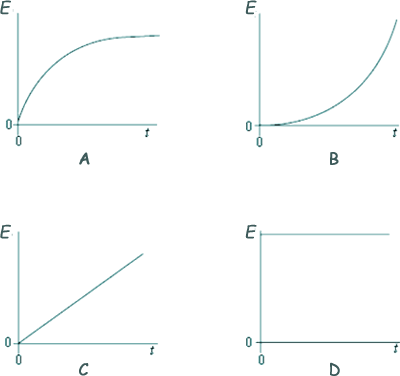Capacitors - Multiple Choice Q11. When switch S in the circuit is closed, the capacitor C is charged by the battery to a pd V0.
Which graph best shows how the pd across the capacitor varies with time, t, after S is opened?
The capacitor is required to supply a constant current of 1.0μA and can be used until the potential difference across it falls by 10%. How long can the
capacitor be used for before it must be recharged?
Q13. When a capacitor discharges through a resistor it loses 50% of its charge in 10 s. What is the time constant of the capacitor-resistor circuit?
Q14. An uncharged capacitor of fixed capacitance is connected in series with a switch and battery. The switch is closed at time t = 0. Which graph, A to D, shows how the energy, E, stored by the capacitor, changes with time, t, after the switch is closed?
Q15.The voltage across a capacitor falls from 10 V to 5 V in 48 ms as it discharges through a resistor. What is the time constant of the circuit?
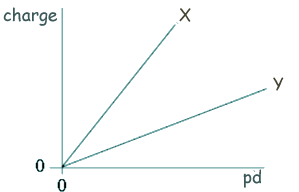
Q16. The graph shows how the charge stored by each of two capacitors, X and Y, increases as the pd across them increases. Which one of the following statements is correct?
Q17. A 1000 μF capacitor and a 10 μF capacitor are charged so that the potential difference across each of them is the same. The charge stored in the 1000 μF capacitor is Q1 and the charge stored in the 10 μF capacitor is Q2. What is the ratio Q1/Q2?
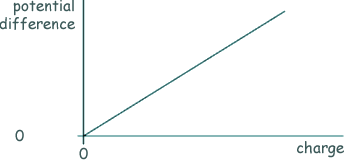
Q18. The graph shows how the potential difference across a capacitor varies with the charge stored by it.
Which one of the following statements is correct?
Q19. An initially uncharged capacitor of capacitance 10 μF is charged by a constant current of 200 μA. After what time will the potential difference across the capacitor be 2000V?
Q20. A 1000 μF capacitor, X, and a 100 μF capacitor, Y, are charged to the same potential difference. Which row, A to D, in the table gives correct ratios of charge stored and energy stored by the capacitors?
|
Follow me...
|