E = mc2 - mass energy conversion
Q5.
(a) Calculate the binding energy, in MeV, of a nucleus of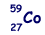 given that
given that
the nuclear mass of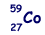 = 58.93320 u
= 58.93320 u
[3 marks]
(b) A nucleus of iron  decays into a stable nucleus of cobalt
decays into a stable nucleus of cobalt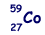 .
.
It decays by β− emission, followed by the emission of γ-radiation as the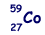 nucleus de-excites into its ground state.
nucleus de-excites into its ground state.
The total energy released when the  nucleus decays is 2.52 × 10−13 J.
nucleus decays is 2.52 × 10−13 J.
The  nucleus can decay to one of three excited states of the
nucleus can decay to one of three excited states of the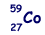 nucleus as shown in the diagram below - the energies of the excited states are shown relative to the ground state.
nucleus as shown in the diagram below - the energies of the excited states are shown relative to the ground state.

Calculate the maximum possible kinetic energy, in MeV, of the β− particle emitted when the  nucleus decays into an excited state that has energy above the ground state.
nucleus decays into an excited state that has energy above the ground state.
[2 marks]
(c) Following the production of excited states of 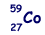 , γ-radiation of discrete wavelengths is emitted.
, γ-radiation of discrete wavelengths is emitted.
(i) State the maximum number of discrete wavelengths that could be emitted.
[1 mark]
(ii) Calculate the longest wavelength of the emitted γ-radiation.
[3 marks]
(Total 9 marks)








