'A' Level Medical Option Questions - X-Rays
Q9.
(a) Explain what is meant by the half-value thickness of lead for X-rays.
The half-value thickness is the thickness of lead needed to reduce intensity of the X-rays of a specific energy  by half
by half 
(b) Calculate the linear attenuation coefficient of lead for 90 keV X-ray photons. half value thickness of lead for 90 keV X-ray photons = 12mm.
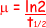

= ln2/(12 x 10-3)
= 58 m-1 
(c) Calculate the thickness of lead needed to reduce the intensity of a beam of 90 keV X-ray photons to 5.0% of the intensity incident on the lead.
I =Ioe– x
x
0.05 = e–57.8x
x = 0.052 m (or 52 mm) 
(Total 6 marks)


