Oscilloscope Questions

Question 1
(a) An oscilloscope is connected across a battery as shown in the diagram.
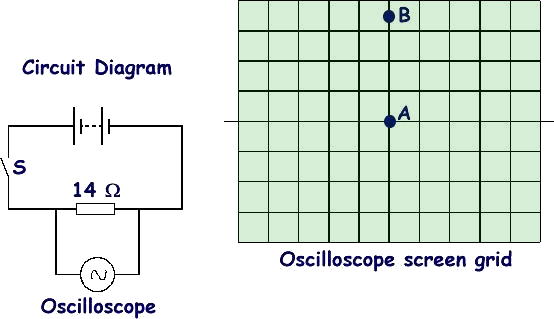
The time base of the oscilloscope is switched off throughout the experiment.
Initially the switch S is open. Under these conditions the spot on the oscilloscope screen is at position A.
Switch S is now closed. The spot moves to B. The voltage gain setting of the oscilloscope is 0.50 V /division.
(i) What does an oscilloscope measure? (1 mark)
(ii) What value does the movement of the spot from A to B represent? (3 marks)
(iii) Given that:
Potential difference (volts) = current (amps) x resistance (ohms)
calculate the current that is flowing through the resistor. (3 marks)
(b) The time base is now switched on. What would you see on the screen:
(i) When switch S was open
(ii) When switch S was closed.
(3 marks) |
(c) The oscilloscope is disconnected from the battery and connected across a mains voltage supply - an alternating voltage source of rms value 230 V and peak value of 330V.
(i)  Sketch the grid on the right and draw what you would expect to see on the oscilloscope screen, if the time base is switched off and the voltage sensitivity is altered to 100 V /div. (3 marks) Sketch the grid on the right and draw what you would expect to see on the oscilloscope screen, if the time base is switched off and the voltage sensitivity is altered to 100 V /div. (3 marks)
(ii) Describe what you would see on the screen if the timebase was then switched on. (2 marks)
(Total 15 marks)
|
Question 2
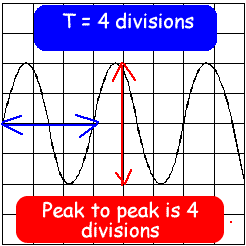 An alternating current (a.c.) source is connected to a 12 W resistor to form a complete circuit. The trace obtained on an oscilloscope connected across the resistor is shown.
An alternating current (a.c.) source is connected to a 12 W resistor to form a complete circuit. The trace obtained on an oscilloscope connected across the resistor is shown.
The oscilloscope settings are:
Y sensitivity 4.0 mV per division and
time base 2.0 s per division.
(a)
(i) Determine the peak to peak voltage of the a.c. source. (3 marks)
(ii) Hence determine the peak voltage. (1 mark)
(iii) Determine the time period of the a.c. signal.
(3 marks)
(iv) Hence calculate the frequency of the a.c. signal. (3 marks)
(b) Given that:
Peak Voltage (volts) = Peak Current (amps) x resistance (ohms)
calculate the peak current that is flowing through the resistor. (3 marks)
(Total 13 marks)
Click here for the answers




 Sketch the grid on the right and draw what you would expect to see on the oscilloscope screen, if the time base is switched off and the voltage sensitivity is altered to 100 V /div. (3 marks)
Sketch the grid on the right and draw what you would expect to see on the oscilloscope screen, if the time base is switched off and the voltage sensitivity is altered to 100 V /div. (3 marks)  An alternating current (a.c.) source is connected to a 12 W resistor to form a complete circuit. The trace obtained on an oscilloscope connected across the resistor is shown.
An alternating current (a.c.) source is connected to a 12 W resistor to form a complete circuit. The trace obtained on an oscilloscope connected across the resistor is shown. 


