The Reflecting Telescope Concave mirrors can be used to project a real image, therefore the image can be recorded on film or used as an image by another viewing system. The intermediate image can therefore be enlarged. All large telescopes in the world's observatories use reflection over refraction. The largest optical telescope in the world has a 10.5 m diameter concave parabollic mirror arrangement made up of many segments. An optical reflector requires many tonnes of glass to make. It takes a considerable cooling time to 'set' and then many hundred of hours were spent grinding it to the perfect parabollic shape. It is silvered with a few grams of aluminium on the inner curved surface so that the light is reflected not refracted. The advantages of a front-silvered concave mirror over a lens system are:
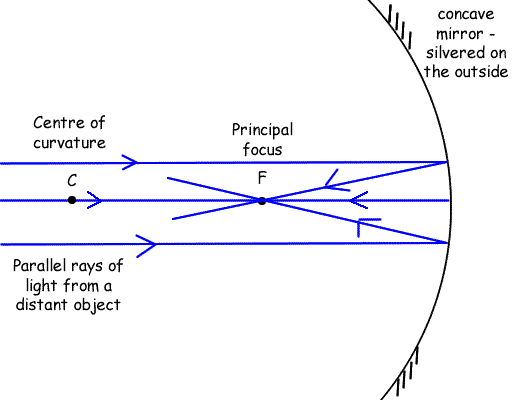
Ray diagrams of curved mirrorsSpherical mirrors are easy to produce, but the image can be distorted by spherical aberration, so a parabolic shape is used to give perfect focusing but in questions you will be set assume the mirror is spherical - you can then use a compass to construct the diagram. As the focal length of a concave mirror is half the radius of curvature of that mirror, when you construct a diagram of a curved mirror system you need to make the diamater of the circle you use to construct the mirror twice the size of the focal length you wish to portray. The rays should be directed towards the centre - area of least spherical abberation. But when labelling your mirror, label it as parabolic!
The Newtonian Reflecting TelescopeLight is reflected to an eyepiece at the side of the telescope.
The Cassegrain TelescopeThe eyepiece is at the back of the telescope. The hole in the centre of the mirror does not affect the viewing ability.
|
Follow me...
|