Power
P
= 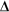 W/t
W/t
Where :
 P = power in
watts (W)
P = power in
watts (W)
 ΔW = work done(or energy expended) in joules (J)
ΔW = work done(or energy expended) in joules (J)
 t = time in
seconds (s)
t = time in
seconds (s)
Now
 W = FΔs (Force x distance moved)
W = FΔs (Force x distance moved)
So
 P = FΔs/t
P = FΔs/t
 But Δs/t = velocity = v
But Δs/t = velocity = v
So
P = Fv
Definitions
 Power is the energy (or
work done) divided by the time that the energy was expended over.
Power is the energy (or
work done) divided by the time that the energy was expended over.
 Power is the rate
at which work is done (how fast it can be done), or the rate at which energy is transferred to another form. The faster a machine can complete a task the more powerful it is.
Power is the rate
at which work is done (how fast it can be done), or the rate at which energy is transferred to another form. The faster a machine can complete a task the more powerful it is.
 Power is measured
in joules per second. A joule per second is a watt (W).
Power is measured
in joules per second. A joule per second is a watt (W).

We tend to think of
things 'having a lot of energy' when they are in effect 'powerful'....
that is because they can work quickly.The higher the wattage of a system
the faster it can do work.
For example a 100W bulb is brighter than a
40W one because it transfers the electrical energy to light energy at
a faster rate.... therefore more photons hit your eye per second and you
think of it as brighter.
Another equation for
power is:
P =
IV
from electricity we know that
I
= Q/t
therefore:
P =
QV/t
Now,
E = QV (energy transfered by the electricity)
so again we have that
power = rate of energy transfer
Useful
link
Physics
classroom (most suitable for A level students).


