Interference Questions Q1.
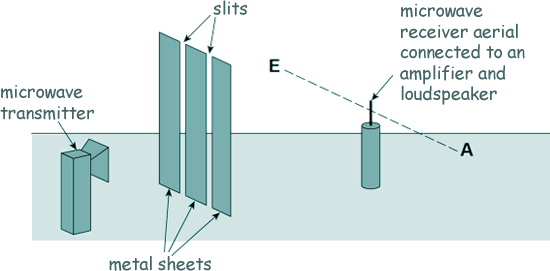
The diagram above shows an arrangement used to investigate double slit interference using microwaves. The following diagram shows the view of the arrangement from above.
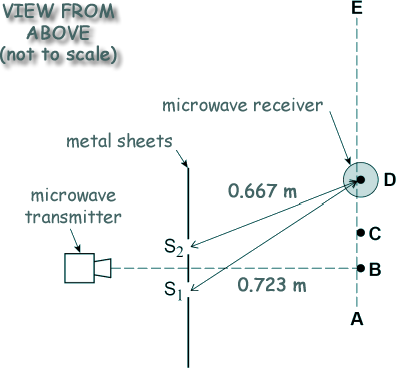
The microwaves from the transmitter are polarised. These waves are detected by the aerial in the microwave receiver (probe). The aerial is a vertical metal rod. The receiver is moved along the dotted line AE. As it is moved, maximum and minimum signals are detected. Maximum signals are first detected at points B and C. The next maximum signal is detected at the position D shown above. The diagram shows the distances between each of the two slits, S1 and S2, and the microwave receiver when the aerial is in position D. S1D is 0.723 m and S2D is 0.667 m. (a) Explain why the signal strength falls to a minimum between B and C, and between C and D. The waves each travel a different distance as they travel from the metal sheet to the transmitter. If the path difference is an even number of half-wavelengths the waves will constructively interfere to a maximum level, but if the path difference is an odd number of wavelengths maximum destructive interference will occur. The path difference for the two waves gives rise to a phase difference [3 marks] (b) Determine the frequency of the microwaves that are transmitted. At D there is a path difference of two wavelengths. 0.723 - 0.667 = 2λ λ = 0.056/2 = 0.028 m c = fλ f = 3.0 x 108/0.028 f = 1.07 x 1010 Hz [3 marks] (c) The intensity of the waves passing through each slit is the same. Explain why the minimum intensity between C and D is not zero. Intensity decreases with distance. [2 marks] (d) The vertical aerial is placed at position B and is rotated slowly through 90° until it lies along the direction AE. State and explain the effect on the signal strength as it is rotated. The signal decreases to zero. [3 marks] (11 marks total) |
Follow me...
|