Radioactivity: Multiple Choice Questions Q1. Which of the following best describes the decay constant for a radioisotope?
Q2. After 64 days the activity of a radioactive nuclide has fallen to one sixteenth of its original value. Calculate the half-life of the radioactive nuclide.
Q3. Radioactive decay is described as being spontaneous. In this context spontaneous means:
Q4. The ionising properties of radiations determine their penetration power.
Q5. Protactinium has a half life of 70s. A sample of protactinium is prepared and monitored over a period of time. Which of the following statements is correct?
Q6. Which of the following does not contribute to background radiation?
Q7. A radioactive source is placed 2.0 cm from a detector. The count rate decreases slightly if a sheet of paper is inserted between the source and the detector. It is reduced to background radiation level if the sheet of paper is replaced by a 1.0 cm thick sheet of aluminium. Deduce what forms of radiation the source emits:
Q8. Before carrying out a radioactivity experiment it is necessary to carry out a background radiation count (so that you can calculate the background count rate). The value of that count is not affected by:
Q9. Within a school laboratory you should always handle radioactive sources with long handled tongs and keep the time of use to a minimum. Choose from the choices below which form of radiation this safety advice most applies to, and for which reason.
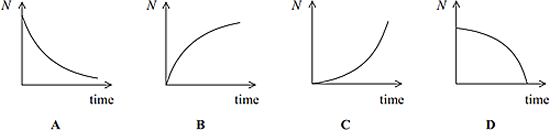
Q10. Some rocks contain lead as a product of radioactive decay. Via one such decay chain a fixed quantity of polonium decays to a stable isotope of lead. Which sketch graph best shows the number of lead atoms (N) in the sample as time progresses?
Q11. The sodium isotope Which line, A to D, in the table below correctly represents the production of
Q12. Artificial radioactive nuclides are manufactured by placing naturally-occurring nuclides in a nuclear reactor. They are made radioactive in the reactor as a consequence of bombardment by:
Q13. A nucleus of a particular element decays, emitting a series of α and β– particles. Which of the following series of emissions would result in an isotope of the original element?
Q14. A Geiger counter is placed near a radioactive source and different materials are placed between the source and the Geiger counter. The results of the tests are shown in the table.
What is the radiation emitted by the source?
Q15. Nobelium-259 has a half-life of 3500 s. What is the decay constant of nobelium-259?
Q16. A pure sample of nuclide X containing N nuclei has an activity A. The half-life of X is 6000 years. A pure sample of nuclide Y containing 3N nuclei has an activity 6A. What is the half-life of nuclide Y?
Q17. Cobalt-60 has a half-life of 5.27 years. What is the total activity of 1.0 g of cobalt-60?
Q18. When a nucleus of the radioactive isotope How many protons and neutrons are there in the resulting daughter nucleus?
|
Follow me...
|