Particle Physics Questions : Multiple Choice
Q1. What are the numbers of hadrons, baryons and mesons in an atom of
There are 3 protons and 4 neutrons - which are baryons and hadrons There are no mesons! Q2. A radioactive nucleus emits a β– particle then an α-particle and finally another β– particle. The final nuclide is:
Beta emission a neutron changes to a proton - two betas so the proton number increases by two. Alpha emission means two protons leave the nucleus (along with two neutrons) so the proton number decreases by two. Overall effect - no change in proton number - same element!
Q3. The nucleus of What is the product nucleus?
Q4. Electron capture can be represented by the equation: p + e- → X + YWhich row correctly identifies X and Y?
Q5. A calcium ion is formed by removing two electrons from an atom of What is the specific charge of the calcium ion?
Q6. The table below links exchange particles with nuclear processes. Select the line that does not give the correct exchange particle for the process.
Q7. Select the line that gives the correct category and quark combination for the particle.
Q8. Select the incorrect statement about muons from the following.
Q9. Which of the following nuclei has the smallest specific charge?
Q10.
Q11.
Q12.
Q13.
Q14. Which of the following is not true?
Q15. Which equation shows the process of annihilation?
Q16. Which of the following is not made of quarks?
Q17. What is the quark structure for antiprotons?
Q18. The equation represents the weak interaction between a negative pion and a proton. π− + p → Ko + X What is the charge, baryon number and strangeness of particle X?
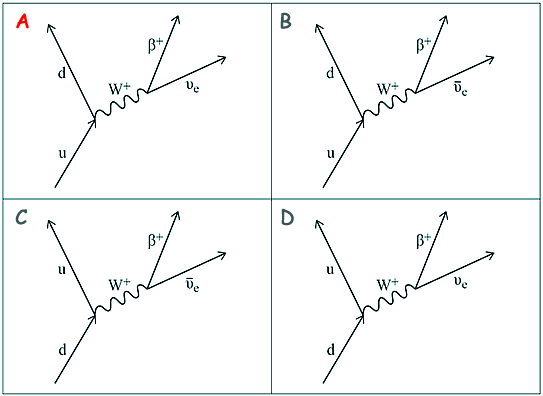
See here for notes on strange particles. Q19. Which diagram represents the process of beta-plus decay?
In positron decay a proton becomes a neutron: p so, quark change is: uud u Therefore it is either choice A or B To balance leptons we need a lepton to be formed as well as the antilepton (positron) - so choice A is correct.
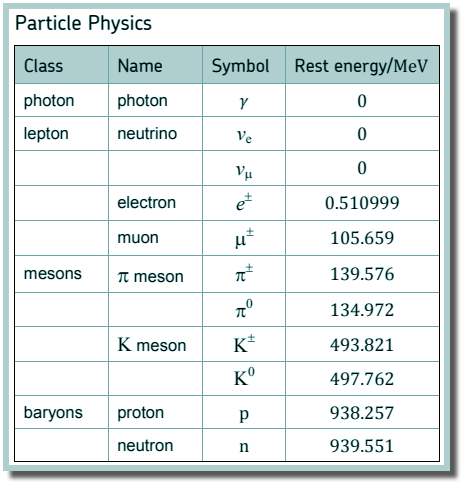
Q20. Two gamma photons are produced when a muon and an antimuon annihilate each other. What is the minimum frequency of the gamma radiation that could be produced?
Sum of rest energies = 2 x 105.659 MeV This is changed to electromagnetic energy in two identical gamma rays travelling in opposite directions. Each gamma ray therefore has energy of 105.659 MeV 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19J Therefore the energy of each gamma ray is 105.659 x 106 x 1.6 x 10-19 = 1.69 x 10-11 J E = hf f = E/h f = 1.69 x 10-11/(6.63 x 10-34) f = 2.55 × 1022 Hz Choice C
|
Follow me...
|