Momentum - Multiple choice Multiple choice questions should take you just under 2 minutes a question! Only one of the choices is correct. Q1. Which one of the following statements is correct? The force acting on an object is equivalent to:
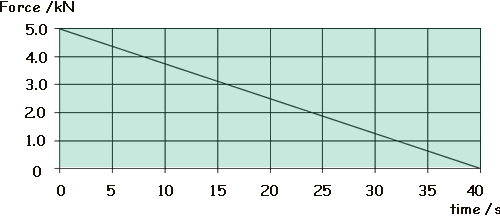
Q2. The graph shows how the force on a glider of mass 2000 kg changes with time as it is launched from a level track using a catapult.
Assuming the glider starts at rest what is its velocity in ms-1 after 40 s?
Q3. A gas molecule of mass m in a container moves with velocity v. If it makes an elastic collision at right angles to the walls of the container, what is the change in momentum of the molecule?
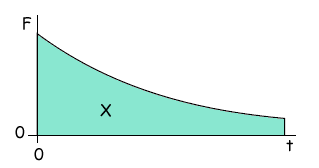
Q4. The graph shows the variation with time, t, of the force, F, acting on a body.
What physical quantity does the area X represent?
Q5. Water of density 1000 kg m–3 flows out of a garden hose of cross-sectional area 7.2 × 10–4m2 at a rate of 2.0 × 10–4m3 per second. How much momentum is carried by the water leaving the hose per second?
Q6. Which row, A to D, in the table correctly shows the quantities conserved in an inelastic
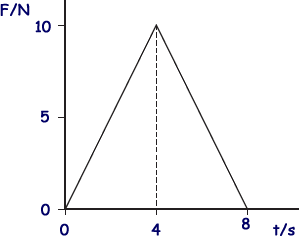
Q7. A ball of mass 2.0 kg, initially at rest, is acted on by a force F which varies with time t as shown by the graph. What is the velocity of the ball after 8.0 s?
Q8. A body X moving with a velocity v makes an elastic collision with a stationary body Y of equal mass on a smooth horizontal surface.
Which line, A to D, in the table gives the velocities of the two bodies after the collision?
Q9. Which of the following is a scalar quantity?
Q10. A car of mass 580 kg collides with the rear of a stationary van of mass 1200 kg. Following the collision, the van moves with a velocity of 6.20 m s−1 and the car recoils in the opposite direction with a velocity of 1.60 m s−1 . What is the initial speed of the car?
Q11. A bullet of mass 10 g is fired with a velocity of 100 ms–1 from a stationary rifle of mass 4.0 kg. Consider the rifle and bullet to be an isolated system. Calculate the recoil velocity of the rifle and the total momentum of the rifle and bullet just after firing.
Q12. Which row correctly states whether momentum, mass and velocity are scalar or vector quantities?
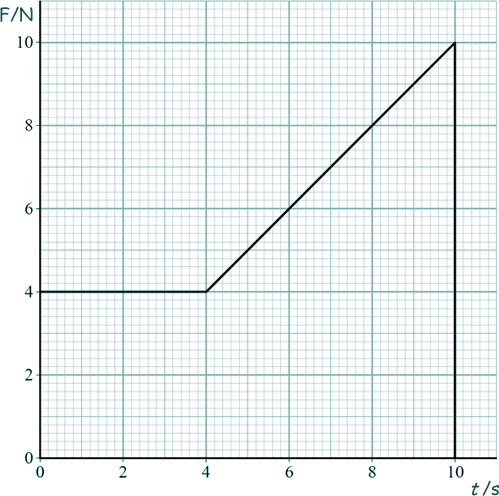
Q13.The graph shows how the force F applied to an object varies with time t.
What is the momentum gained by the object from t = 0 to t = 10 s? |
Follow me...
|