Magnetic Fields Questions
Q1. Here is a diagram of a mass spectrometer
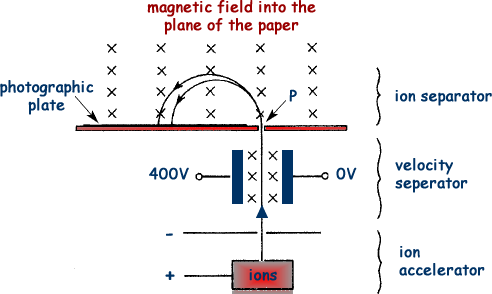
(a) The magnetic field strength in the velocity selector is 0.14T and the electric field strength is 20 kVm–1.
(i) Define the unit for magnetic flux density, the tesla.
The Tesla is the unit of flux density. It is the flux density, acting perpendicular to a wire, that produces a force of 1N on a metre of wire that is carrying a current of 1A .
that produces a force of 1N on a metre of wire that is carrying a current of 1A .
(2 marks)
(ii) Show that the velocity selected is independent of the charge on an ion.
FE = QV/d
FM = BQv
FE = FM therefore QV/d = BQv
Q cancels so V/d = Bv and
v = V/Bd = E/B 
v is therefore not dependent on Q 
(2 marks)
(iii) Show that the velocity selected is about 140 kms–1
v = E/B
v = 20 x 103/0.14 
= 1.43 x 105
= 140 km s−1 (to 2 sig figs) QED
(1 mark)
(b) A sample of nickel is analysed in the spectrometer. The two most abundant isotopes of nickel are:
 and
and 
Each ion carries a single charge of +1.6 × 10–19 C
The Ni-58 ion strikes the photographic plate 0.28 m from the point P at which the ion beam enters the ion separator.
Calculate:
(i) the magnetic flux density of the field in the ion separator;
Magnetic force acts as a centripetal force:
BvQ = mv2/r
so the magnetic flux density B = mV/rQ
mass of ion:
58 x 1.661 × 10–27 kg = 9.64 x 10-26 kg 
B = (9.64 x 10-26 x 1.43 x 105) / (0.14 x 1.6 × 10–19) = 0.615
B = 0.62 T
(3 marks)
(ii) the separation of the positions where the two isotopes hit the photographic plate.
Radius r of the path is proportional to the mass m of ion
r ∝ m
∴ r1/r2 = m1/m2
r2 = m2/m1 x r1
new radius = 60/58 × 0.140 = 0.145 m 
new diameter = 0.290 m
distance apart = 0.29 - 0.28 = 0.010 m 
(2 marks)
(Total 10 marks)


