Questions on Characteristic Curves - Filament Lamp
Q5. When a filament lamp is switched on it takes 0.50 seconds for the filament to reach its normal operating temperature. The way in which the current changes during the first second after switching on is shown on the graph below.
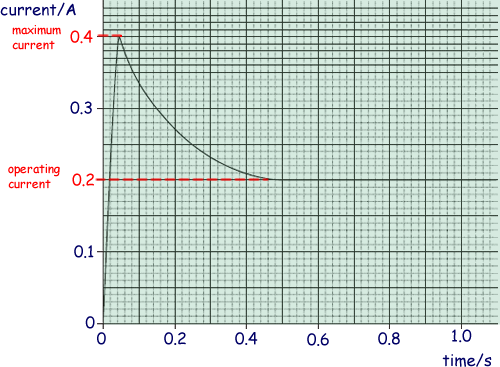
(a) Use the graph to determine the maximum current through the lamp.
0.40 A 
(1 mark)
(b) Assuming that the lamp is connected to a 12V dc supply of a negligible internal resistance,
(i) Calculate the resistance of the lamp when it has reached its normal operating temperature,
V = IR
resistance = V/I
R = 12/0.2
R = 60 Ω 
(1 mark)
(ii) Calculate the power of the lamp when it has reached its normal operating temperature.
power = VI
P = 12 × 0.2
P = 2.4 W 
(1 mark)
(c) Explain why the current through the lamp decreases between 0.05 s and 0.50 s.
When a current passes through a wire electrons interact with the metal lattice. This results in an increase in resistance of the wire and increased heat dissipation which makes the wire rise in temperature. 
The resistance of the filament wire increases as the heat dissipated, because of current flow, causes its temperature to rise. A hotter wire has a higher resistance and therefore the current will decrease as the filament gets hotter until it reaches thermal equilibrium.
(2 marks)
(d) State and explain the change, if any, to the final current through the lamp if it is connected to the same supply with another similar lamp
(i) in series,
The supply voltage is now shared by lamps.  Therefore each lamp will have a lower potential difference across it and therefore the current wil be reduced.
Therefore each lamp will have a lower potential difference across it and therefore the current wil be reduced.
Or
The total circuit resistance is increased  hence will be current reduced.
hence will be current reduced. 
(2 marks)
(ii) in parallel.
The current through the lamps unchanged/stays the same  as both connected directly to the supply and have the full circuit potential difference across each bulb.
as both connected directly to the supply and have the full circuit potential difference across each bulb.
Or
The bulbs being in parallel will result in a total circuit resistance of half of the value before. This will then result in double the current through the power supply  which will split to go through both bulbs. Therefre each bulb will still have the same current going through it as before.
which will split to go through both bulbs. Therefre each bulb will still have the same current going through it as before. 
(2 marks)
(e) State and explain why a filament lamp is most likely to fail as it is switched on.
The resistance of a lamps will be at its lowest value when it is first switched on as the filament wire will be cool and cool metals have lower resitances than hotter ones.
Hence initial current will be larger. 
As the current begins to flow there will be a sudden rapid change in temperature.
This might be enough to melt the filament wire and cause the bulb to 'blow'. 
(2 marks max)
(Total 11 marks)







