Quantum Phenomena - discrete energy levels for electrons
Q7. In a discharge tube a high potential difference is applied across hydrogen gas contained in the tube. This causes the hydrogen gas to emit light that can be used to produce the visible line spectrum as shown below.

The visible line spectrum above has been used to predict some of the electron energy levels in a hydrogen atom.
The energy levels predicted from the visible line spectrum are those between 0 and –3.40 eV in the energy level diagram.
(a) Some of the predicted energy levels are shown below:
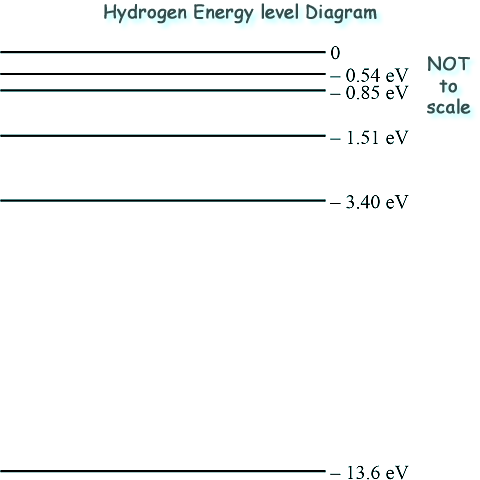
(i) Calculate the energy, in eV, of a photon of light that has the lowest frequency in the visible hydrogen spectrum shown in the diagram.
656 nm = 656 x 10-9m 
c = fλ
E = hf = hc/λ
E = 6.63 x 10-34 x 3.0 x 108/(656 x 10-9) 
E = 3.03 x 10-19 J
E = 3.03 x 10-19/1.6 x 10-19eV
E = 1.9 eV 
[3 marks]
(ii) Identify the state of an electron in the energy level diagram labelled 0.
They are free. 
[1 mark]
(iii) Identify the state of an electron that is in the energy level labelled –13.6 eV.
It is in the ground state  (the lowest level/energy state an electron can occupy).
(the lowest level/energy state an electron can occupy).
[1 mark]
(iv) Explain why the energy levels are negative.
To become free of the atom an electron has to reach zero energy. Therefore energy has to be supplied to the electron to free it and the energy it lacks to be free is therefore represented as negative. 
[1 mark]
(b) Discuss how the discharge tube is made to emit electromagnetic radiation of specific frequencies. In your answer you should:
 explain why there must be a high potential difference across the tube
explain why there must be a high potential difference across the tube
 discuss how the energy level diagram predicts the visible line spectrum.
discuss how the energy level diagram predicts the visible line spectrum.
 show how one of the wavelengths of light is related to two of the energy levels in the energy level diagram.
show how one of the wavelengths of light is related to two of the energy levels in the energy level diagram.
Mark |
Criteria |
6 |
All three aspects analysed.
6 marks can be awarded even if there is an error and/or parts of one aspect missing. |
5 |
A fair attempt to analyse all 3 aspects.
If there are a couple of errors or missing parts then 5 marks should be awarded. |
4 |
Two aspects successfully discussed, or one discussed and two others covered partially.
Whilst there will be gaps, there should only be an occasional error. |
3 |
Two aspects discussed, or one discussed and two others covered partially.
There are likely to be several errors and omissions in the discussion. |
2 |
Only one aspect discussed successfully, or makes a partial attempt at 2 or all 3. |
1 |
None of the three aspects covered without significant error. |
0 |
No relevant analysis. |
The following statements are likely to be present.
Reason for high potential difference:
 pd accelerates electrons/produces high speed/high energy electrons in the tube
pd accelerates electrons/produces high speed/high energy electrons in the tube
 electrons have to have sufficient energy to excite the atoms/raise electrons into higher levels
electrons have to have sufficient energy to excite the atoms/raise electrons into higher levels
Relation between spectrum and energy level diagram
 Visible spectrum results from excited electrons moving into the lower level at -3.4 eV
Visible spectrum results from excited electrons moving into the lower level at -3.4 eV
 Each transition results in a photon of light.
Each transition results in a photon of light.
 Energy of photon is the difference in the energies of the two levels
Energy of photon is the difference in the energies of the two levels
 Frequency of light in the spectrum given by ΔE = hf
Frequency of light in the spectrum given by ΔE = hf
Relevant calculation clearly communicated
 Gives an example: eg the lowest frequency is due to a transition from the -1.5 eV level to the -3.4 level.
Gives an example: eg the lowest frequency is due to a transition from the -1.5 eV level to the -3.4 level.
 Uses an energy difference to deduce one of the wavelengths:
Uses an energy difference to deduce one of the wavelengths:
- energy difference in J = 3.0 × 10-19T
- λ = hc/E = 660 nm
[6 marks]
(Total 12 marks)








