Solutions: Atomic Structure
Q15. The table belowcontains five statements that refer to isotopes and some radium isotopes.
|
 |
 |
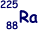 |
 |
Isotope with the smallest mass number
|
|
|
|
|
Isotope with most neutrons in nucleus |
|
|
|
|
Isotope with nucleus which has the largest specific
charge |
|
|
|
|
Isotope decays by β– decay to form 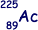 |
|
|
|
|
Isotope decays by alpha decay to form 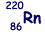 |
|
|
|
|
(a) Complete the table by ticking one box in each row to identify the appropriate isotope for each statement. The first row has been completed for you.
[4 marks]
(b)
(i) An atom of one of the radium isotopes in the table is ionised so that it has a charge of +3.2 × 10–19 C. State what happens in the process of ionising this radium atom.
It has lost two electrons 
[1 mark]
(ii) The specific charge of the ion formed is 8.57 × 105 C kg–1. Deduce which isotope in the table has been ionised. Assume that both the mass of a proton and the mass of a neutron in the nucleus is 1.66 × 10–27 kg.
The charge on the ion is given you in part (i).
Specific charge = charge/mass
mass = charge/specific charge
mass = 3.2 × 10–19/8.57 × 105
mass = 3.73 x 10-25 kg
mass = number of nucleons x 1.66 × 10–27
number of nucleons = 3.73 x 10-25/1.66 × 10–27
number of nucleons = 225 
The isotope is 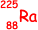


[3 marks]
(Total 8 marks)


