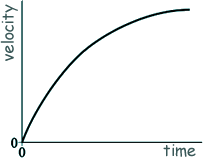
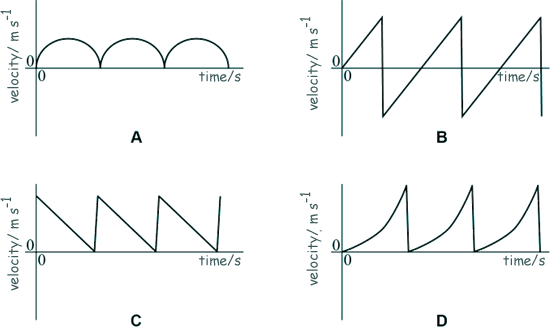Dynamics - Including Equations of Motion Q1. The velocity–time graph for a falling object is shown.
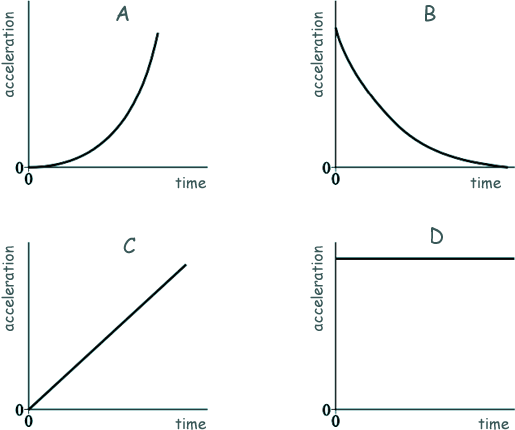
Which of the following shows the corresponding acceleration–time graph?
Q2. A girl jogs at 2.0 m s–1 in a straight line for 30 seconds, turns around and returns to her starting point 20 seconds later. What is her average velocity and average speed?
Q3. A golf ball was hit from the surface of the Moon. The time of flight was 4.0 s. What is the best estimate for the maximum height reached by the ball? Acceleration due to gravity on the Moon = 1.6 m s–2
Q4. A deep-space probe travelling forward at constant speed is briefly acted on by a force at right angles to its motion. What is the effect of this force on the forward speed and sideways speed of this probe?
Q5. A roller coaster car is raised to a height of 65 m and released from rest. What is the maximum possible speed of the car?
Q6. Which row gives two features of graphs that provide the same information?
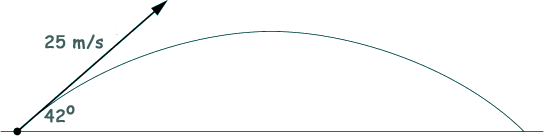
Q7. The diagram shows the path of a projectile launched from ground level with a speed of 25 m s −1 at an angle of 42° to the horizontal.
What is the horizontal distance from the starting point of the projectile when it hits the ground?
Q8. Which graph best represents the velocity–time graph for a ball that is dropped from rest and bounces repeatedly?
Q9. Two identical balls, X and Y, are at the same height and a horizontal distance of 25 cm apart. X is projected horizontally with a velocity of 0.10 m s–1 towards Y at the same time that Y is released from rest. Both X and Y move freely in the absence of air resistance. What is the distance between the balls 1.0 s later?
|
Follow me...
|