A level: Kinetic Theory Questions
Q17. A number of assumptions are made when explaining the behaviour of a gas using the molecular kinetic theory model.
(a) State one assumption about the size of molecules.
The volume of the gas molecules is negligible
Or
molecules are point masses
Or
the molecules are small compared to the total volume occupied by of the gas 
[1 mark]
(b) The graph shows how the pressure changes with volume for a fixed mass of an ideal gas.
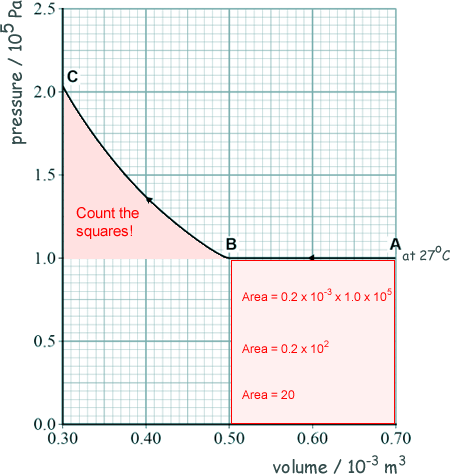
At A the temperature of the gas is 27 oC.
The gas then undergoes two changes, one from A to B and then one from B to C.
(i) Calculate the number of gas molecules trapped in the cylinder using information from the initial situation at A.
Using N = PV/kT
T = 27 + 273 = 300K
N = 1.0 x 105 x 0.70 x 10-3 /(1.38 x 10-23 x 300  )
)

N = 1.69 x 1022 molecules
N = 1.7 x 1022 molecules 
OR
Using n = PV/RT
n = (1.0 x 105 x 0.70 x 10-3 / 8.31 x 300  )
)
n = 0.028 mol
N = n NA
N = 0.028 x 6.02 x 1023
N = 1.69 x 1022 molecules
N = 1.7 x 1022 molecules 
[2 marks]
(ii) Calculate, in K, the change in temperature of the gas during the compression that occurs between A and B.
Using TB = TA VB / VA
TB = 300 × 0.50 / 0.70 = 214 K 
Or
TB = PV/Nk
TB = 1.0 x 105 x 0.50 x 10-3 /(1.38 x 10-23 x 1.69 x 1022)
TB = 214 K 
Or
TB = PV/nR
TB= 1.0 x 105 x 0.50 x 10-3/(0.028 x 8.31) = 215 K 
Change in temperature ΔT = 214 (or 215) – 300
ΔT = – 86 (or 85) K 
[2 marks]
(iii) Deduce whether the temperature of the gas changes during the compression of the gas from B to C.
If the temperature remained constant then PV = constant:
PC = PB VB / VC
PC = 1.0 x 105 x 0.50 x 10-3/0.30 x 10-3
PC = 1.7 x 105 Pa 
But the pressure at C is higher than this so the temperature at C must be different/higher /not constant. 
Or
You could say if the temperature remained constant PCVC would equal PBVB and then show that is not the case or do a full calculation using PV /T = constant.
[2 marks]
(iv) Compare the work done on the gas during the change from A to B with that from B to C.
Work done on gas from A to B is found by using W = PΔV
W = area under the graph 
Work done = 1.0 × (0.70 – 0.50) × 10-3 )
Work done = 20 J 
Calculating the area indicated corresponds to the additional work done on the gas from B to C
166 mm2 (where 1 mm2 = 0.05 J) = 8.3 J 
( 8.0 – 10.0 J was allowed)
Or
The total work done from B to C (566 mm2 where 1 mm2 = 0.05 J) = 28.3 J
( 28.0 – 30.0 J was allowed)
[3 marks]
(10 marks total)







