Particle Questions that include Feynman Diagrams
Q2.
(a) An electron and a positron travelling with equal speeds meet head-on and annihilate, releasing 2.0 × 106 eV of energy. This energy is shared equally by two photons. Calculate the energy, in J, of each photon.
energy of each photon = 2.0 x 106/2 eV = 1.0 x 106 eV
1.0 × 106 × 1.6 × 10–19 = 1.6 × 10–13 J
(1 mark)
(b) Complete the table by writing true or false in the right hand column. The first two lines have been completed as an example.
a neutron is a fundamental particle |
false |
an antineutron is not a fundamental particle |
true |
a neutron is a stable particle |
false see here |
an antineutron is an unstable particle |
true |
a neutron has a rest mass of 1.67 × 10–27 kg |
true |
a antineutron has a rest mass of –1.67 × 10–27 kg |
false (no such thing as negative mass!) |
a neutron has no charge |
true |
an antineutron has a charge of 1.60 × 10–19 C |
false |
One mark for each section that is correct (each pair of statements) 


(3 marks)
(c)
(i) The exchange particle responsible for the weak interaction is either a W boson or a Z boson. Give the name of another exchange particle and the interaction for which it is responsible.
(particle) gamma ray or photon  (interaction) electromagnetic
(interaction) electromagnetic 
[or gluons or π mesons, with strong nuclear force]
[or gravitons with gravity]
(ii) An antineutrino may be detected via its weak interaction with a proton as shown in the Feynman diagram below. Complete the labelling on the diagram.
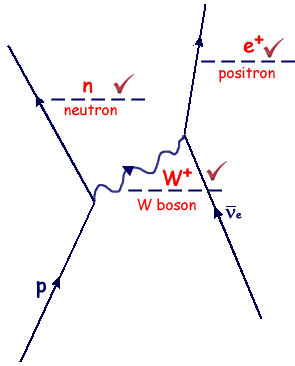
(5 marks)
(Total 9 marks)


