GCSE Questions - Waves
Q18. Look at this diagram of a water wave.
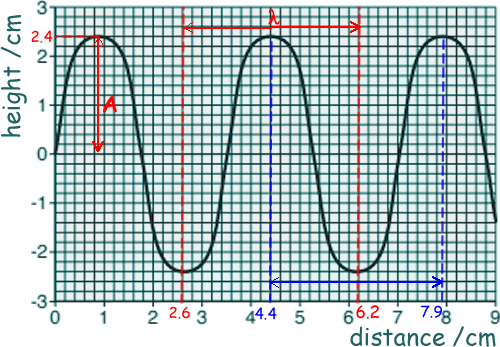
(a)
(i) What is the wavelength of this wave?
λ = 6.1 - 2.6 = 3.6 cm (using the 'red' lines on the diagram) 
OR
λ = 7.9 - 4.5 = 3.5 cm (using the 'blue' lines on the diagram)
[1 mark]
(ii) What is the amplitude of this wave?
A = 2.4 cm 
[1 mark]
(iii) The wavelength of the wave is changed to 25cm. Two waves are produced each second.
Calculate the speed of the wave in m/s.
λ = 25 cm = 0.25 m 
f = 2 Hz 
speed = fλ
speed = 0.25 x 2 = 0.5 m/s 
[4 marks]
(b) Water waves are transverse and sound waves are longitudinal.
(i) Describe how water particles move in a transverse water wave.
The water particles move 'up and down'/oscillate/vibrate at right angles to the direction of travel of the wave. 
[1 mark]
(ii) Describe how air particles move in a longitudinal sound wave.
The aire particles move 'backwards and forwards'/oscillate/vibrate parallel to the direction of travel of the wave. 
[1 mark]
(c) Visible light is part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
(i) Name a wave in the electromagnetic spectrum that has a longer wavelength than red light.
One of the following:
Radio / infra-red / microwave 
[1 mark]
(ii) Name a wave in the electromagnetic spectrum that has a higher frequency than violet light.
One of the following:
Ultra-violet / X-rays / gamma-rays 
[1 mark]
(iii) State two uses of gamma-rays.
Any two from: 

Radiotherapy / treating cancer tumours/ killing cancer cells
Irradiating food / sterilisation of instruments / killing bacteria or (harmful) microorganisms
As a tracer / medical imaging
Scanning metals / non-destructive testing (NDT)
[2 marks]
(Total 12 marks)







