GCSE level questions on the Earth in Space
Q18.

(a) A main sequence star in a distant galaxy is the same size and mass as the Sun.
Explain why the star is stable while it is in the main sequence stage of its life cycle.
In the main sequence stage the gravitational force inwards, and forces as a result of fusion reactions/fusion pressure outwards,  are in equilibrium/balanced.
are in equilibrium/balanced. 
[2 marks]
(b) Describe what will happen to the star between the main sequence stage and the end of the star's life cycle.
You should include the names of the stages in the life cycle of the star in your answer.
When the star begins to run out of hydrogen for the fusion process it's core will collapse, get hotter and the outer layer will expand. The star becomes a red giant.  It will then collapse leaving some of its outermost layers as space debris - the core becoming a white dwarf,
It will then collapse leaving some of its outermost layers as space debris - the core becoming a white dwarf,  and finally it will cool to become a black dwarf.
and finally it will cool to become a black dwarf. 
[3 marks]
(c) The sketch graph below shows how the speed of galaxies moving away from Earth varies with the distance of the galaxies from Earth.
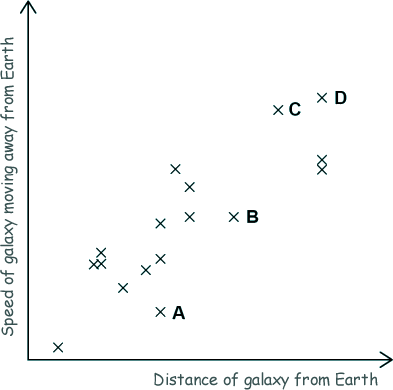
Choose the letter representing the galaxy that would show the smallest observed change in the wavelength of visible light.
Give a reason for your answer.
A  - The further a star is away from us the greater its 'red shift' - meaning we see light from it shifted the most to the red end of the spectrum. Therefore A would show the smallest change in the wavelength of the visible light it emits.
- The further a star is away from us the greater its 'red shift' - meaning we see light from it shifted the most to the red end of the spectrum. Therefore A would show the smallest change in the wavelength of the visible light it emits.
[2 marks]
(Total 7 marks)


