GCSE Questions: Radioactivity
Q17. A teacher demonstrates properties of radioactive particles by performing an experiment about radioactivity in class.
She demonstrates how different types of radiation are absorbed by putting different barriers between the source and the Geiger-Müller tube.
She uses four different radioactive sources, which she calls A, B, C and D in the experiment.
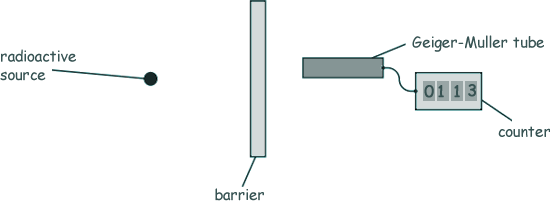
(a) Suggest two safety precautions that the teacher should use when performing this experiment to a class.
Any two from: 

 Keeping herself and her students a safe distance from the sources
Keeping herself and her students a safe distance from the sources
 Place a lead glass screen between the experiment and her students
Place a lead glass screen between the experiment and her students
 Using tongs to handle the source
Using tongs to handle the source
 Ensure she points the sources away from people
Ensure she points the sources away from people
 Keep the sources in sealed lead containers when not in use
Keep the sources in sealed lead containers when not in use
 Keep the exposure time as short as possible
Keep the exposure time as short as possible
[2 marks]
(b) The teacher selects source A to investigate first. She uses the Geiger-Müller tube to measure the count rate (counts per minute) for different barriers. She then repeats the experiment with source B, source C and then source D.
Here are the results.
Source |
Count rate using different barriers |
Paper |
Aluminium |
Lead |
No barrier |
A |
113 |
112 |
22 |
112 |
B |
20 |
21 |
20 |
182 |
C |
162 |
23 |
21 |
164 |
D |
282 |
78 |
24 |
280 |
He also finds that the average count rate with no sources and no barriers is 20.
(i) Which source A, B, C or D emits gamma radiation only? Explain your answer.
Source A  is a sole gamma emitter. Paper and aluminum had no effect on the count, but lead reduced the count significantly (to background level).
is a sole gamma emitter. Paper and aluminum had no effect on the count, but lead reduced the count significantly (to background level).
[2 marks]
(ii) Which source A, B, C or D emits alpha radiation only? Explain your answer.
Source B  is a sole alpha emitter. All of the barriers reduced the count significantly (to background level), therefore even paper could absorb these particles effectively.
is a sole alpha emitter. All of the barriers reduced the count significantly (to background level), therefore even paper could absorb these particles effectively.
[2 marks]
(iii) Which source A, B, C or D could emit both beta and gamma radiation? Explain your answer.
Source D  is a beta and gamma emitter. Paper had noo effect on the count rate, but aluminum reduced the count, absorbing the beta particles and lead reduced the count even more as it absorbed both the beta and gamma radiation.
is a beta and gamma emitter. Paper had noo effect on the count rate, but aluminum reduced the count, absorbing the beta particles and lead reduced the count even more as it absorbed both the beta and gamma radiation.
[2 marks]
(c) The teacher notices that the count rate behind the lead barrier ranges from 20 to 24.
Give two reasons why there are a wide range of results around 22 counts per minute.
Any two from: 

 Radioactive decay is random
Radioactive decay is random
 Variations are more pronounced at low count rates
Variations are more pronounced at low count rates
 Background radiation
Background radiation
[2 marks]
(d) The teacher decides to repeat the experiment. This time she records the number of counts for a much longer time interval for each source. Explain why this is an improvement to the experiment.
Any two from: 

 Larger number of counts - more radiation would be detected
Larger number of counts - more radiation would be detected
 Less variation in count rate - it would smooth out variations
Less variation in count rate - it would smooth out variations
 Gives an average count rate
Gives an average count rate
 Gives more repeatable results - it is more reliable
Gives more repeatable results - it is more reliable
 Makes it easier to decide what the source is
Makes it easier to decide what the source is
[2 marks]
(Total 12 marks)







