GCSE Level Questions: Transformers
Q8. The diagram shows the structure of a traditional transformer.
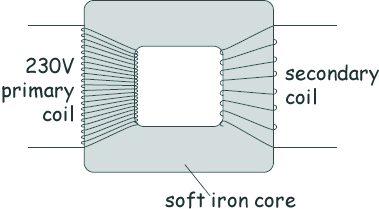
(a) There is an alternating current in the primary coil of the transformer.
State what is produced in the iron core.
A magnetic field  that is changing
that is changing  (or alternating).
(or alternating).
[2 marks]
(b) A transformer has only ten turns of wire on the secondary coil. If the potential difference across the secondary coil is 1.15 V and the potential difference across the primary coil is 230 V
Calculate the number of turns on the primary coil.
Ratio of turns = ratio of potential difference 
Tp/Ts = Vp/Vs
Tp= (VpTs)/Vs
Tp= 230 x 10/1.15
Tp= 2300/11.5
Tp = 200
[3 marks]
(c) In most transformers, the power output is less than the power input. State why.
Transformers are not 100% efficient  - energy/power is lost to the surroundings as heat/sound.
- energy/power is lost to the surroundings as heat/sound.
[1 mark]
(d) Two students investigated how magnets can be used to produce a potential difference.
The students held a coil of wire above a magnet. They quickly lowered the coil so that the magnet was inside the coil, as shown in the diagram.
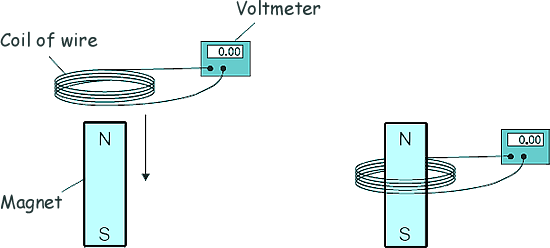
The students recorded the maximum potential difference for coils with different numbers of turns of wire. The results are shown below.
| Number of turns of wire in the coil |
Maximum potential difference / V |
| Results from student 1 |
Results from student 2 |
5 |
0.09
|
0.08 |
10 |
0.20 |
0.15 |
15 |
0.31 |
0.25 |
20 |
0.39 |
0.33 |
25 |
0.51 |
0.39 |
(d)
(i) State the resolution of the voltmeter and give one reason why the resolution of the voltmeter is suitable for this investigation.
The resolution is 0.01 V. 
This is suitable because it is sensitive enough to give a change in the measured potential difference each time the number of turns was changed. If results were measured to only 1 decimal place, there might not be a detectable difference.
If results were measured to only 1 decimal place, there might not be a detectable difference.
[2 marks]
(ii) The two students used exactly the same equipment to carry out their investigations. Both students recorded their results correctly. Give the reason why student 2 got different results from student 1.
Student 2 must have moved the coil more slowly than student 1.
[1 mark]
(iii) The students decided that even though the results were different, there was no need to repeat the investigation. How do the results show that the investigation is reproducible?
Both sets of results show the same pattern or trend 
[1 mark]
(iv) State the name of the process which causes the potential difference to be produced in this investigation.
Electromagnetic induction 
[1 mark]
(e) A transformer has been developed that can be used with many different devices.
Suggest one advantage of having a transformer that can be used with many different devices.
Any one from: 
 more economical/cheaper/convenient for the consumer
more economical/cheaper/convenient for the consumer
 easier/cheaper to replace if broken/lost
easier/cheaper to replace if broken/lost
 since fewer transformers need to be made less resources are used
since fewer transformers need to be made less resources are used
[1 mark]
(12 Marks Total)









