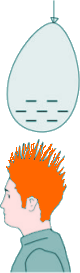
GCSE Level Questions: Magnets and Electromagnets Q3. Ronald stands on a mat made of insulating material. The diagram below shows Ronald's head after rubbing a balloon on his hair. The balloon and hair have become charged.
(a) Describe the force that acts on the Ronald's hair to make it stand on end as shown in the diagram. There is an electrostatic force of attraction There is also an electrostatic force of repulsion [5 marks] (b) An earthed conductor was brought near to Ronald's hand. A spark jumped between the conductor and his hand. The potential difference between the conductor and Ronald was 2.5 kV. The energy transferred by the spark was 0.0050 J Calculate the charge transferred by the spark. E = QV Q = 2.5 kV = 2500 V 0.0050 = Q x 2500 Q = 0.0050/2500 Q = 2.0 x 10-6 Q = 2.0 μC
[4 marks] (c) A defibrillator can transfer a charge to regulate a person's heartbeat.The photo shows a defibrillator.
When the defibrillator is in use, a potential difference of 4800 V is applied across the person's chest. A charge of 0.16 coulombs passes through the person's chest in 4.0 ms Calculate the resistance of the person's chest. I = Q/t I = 0.16/(4.0 x 10-3) I = 40 A V = IR R = V/I R = 4800/40 R = 120 [5 marks] (TOTAL 14 marks) |
Follow me...
|