GCSE questions on refraction and TIR
Q4. The diagram shows how a ray of light from a laser travels along an optical fibre.
(a) Explain why the ray of light stays within the optical fibre.
It stays within the fibre because the angle of incidence on the fibre boundary is greater than critical angle  for the material. It therefore suffers total internal reflection.
for the material. It therefore suffers total internal reflection.
(2 marks)
(b) The material used to make the optical fibre has a refractive index 'n' of 1.50.
Calculate the critical angle 'c' of this material given that sin c = 1/n
sin c = 1/1.50
c = 41.8o
(2 marks)
(c) Different wavelengths of light can be used to transmit information along optical fibres.
The diagram below shows how the percentage of incident light transmitted through a fibre varies with the wavelength of light and the length of the fibre.
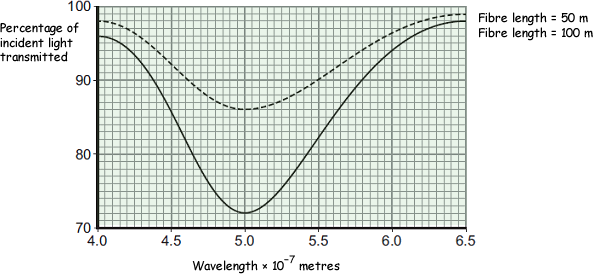
Compare the percentages of incident light transmitted through the two different fibres over the range of wavelengths shown.
 For both fibres increasing the wavelength of light to 5.0 x 10-7 metres, decreases the (percentage) transmission.
For both fibres increasing the wavelength of light to 5.0 x 10-7 metres, decreases the (percentage) transmission. 
 At the wavelength of light to 5.0 x 10-7 metres a minimum transmission occurs of 72% of the incident light for both fibres.
At the wavelength of light to 5.0 x 10-7 metres a minimum transmission occurs of 72% of the incident light for both fibres.
 As the wavelength increases beyond the wavelength of light to 5 x 10-7 metres the transmission increses reaching a higher transmission ot the wavelength of light to 6.5 x 10-7 metres than was the case at the wavelength of light to 4.0 x 10-7 metres.
As the wavelength increases beyond the wavelength of light to 5 x 10-7 metres the transmission increses reaching a higher transmission ot the wavelength of light to 6.5 x 10-7 metres than was the case at the wavelength of light to 4.0 x 10-7 metres. The 100m cable has the most gain.
The 100m cable has the most gain.

(3 marks)
(Total 7 marks)








