GCSE level optics questions
Q21. The diagram shows a human eye.
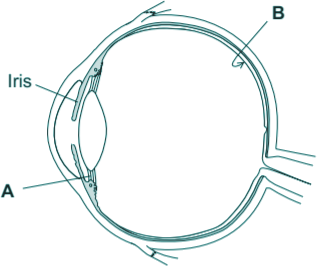
(a) Label the parts A and B on diagram.
[2 marks]
(b) State the function of the iris.
[1 mark]
(c)
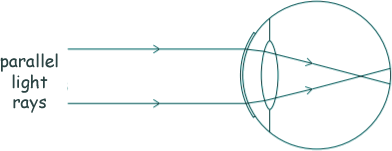
(i) Give the name of the defect of vision shown in the diagram above.
[1 mark]
(ii) A concave (diverging) lens can be used to correct the defect of vision shown in the diagram.
Complete the ray diagram below to show how a concave lens produces an image of the object. Use an arrow to represent the image.
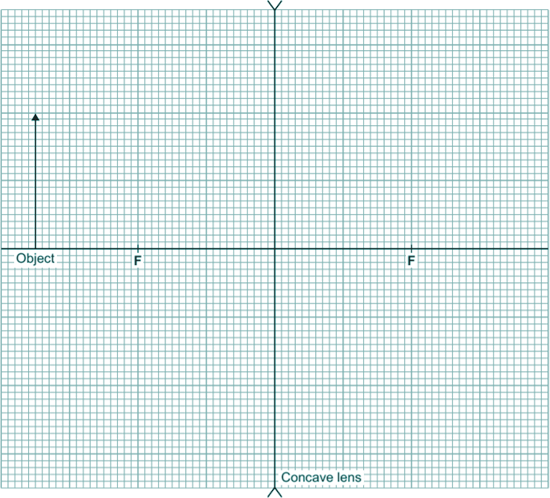
[3 marks]
(d) It is important that muscles can change the power of the lens in the eye. State why.
[1 mark]
(e) The 'power range' of an eye lens is the difference between the maximum and minimum power of the lens.
The graph shows how the power range of an eye lens changes with age.
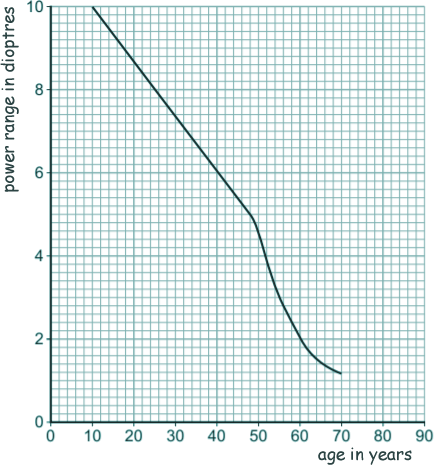
(i) Use data from Figure 9 to calculate the maximum change that can happen to the focal length of the eye lens for a 60-year-old person. Give the unit.
[2 marks]
(ii) Compare the change in power range of the eye lens between the ages of 10 and 30 with that between the ages of 50 and 70.
[3 marks]
(iii) Use the graph to suggest the power range of the eye lens for a 90-year-old person.
[2 mark]
(Total 15 marks)











