GCSE level optics questions Q20. (a) Some people have an eye defect called long sight.
[1 mark]
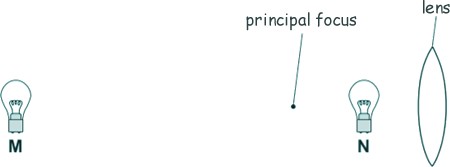
[1 mark] (b) A light bulb is placed between a convex lens and the principle focus of this lens, at position N shown in the diagram. The light bulb is then moved to position M, a large distance from the lens.
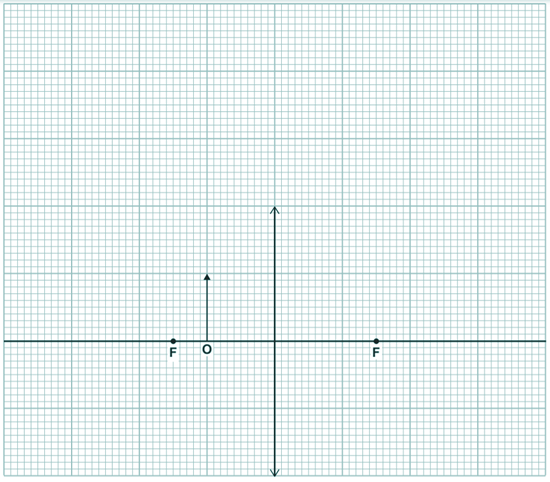
Describe how the nature of the image formed changes as the light bulb is moved from position N to position M. [3 marks] (c) An object, O, is very near to a convex lens, as shown in Figure 15. Complete the diagram below to show how rays of light from the object form an image.
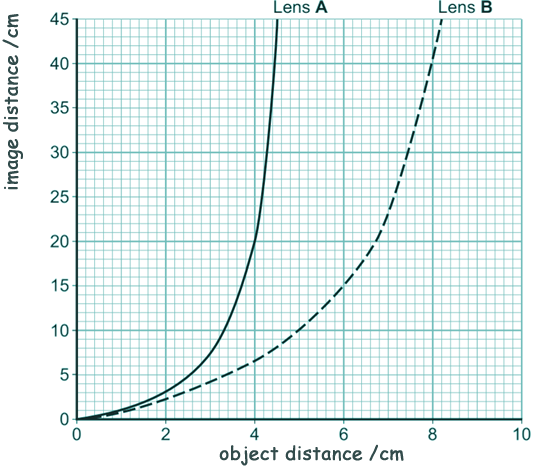
[3 marks] (d) The object distance is the distance from an object to the lens. The image distance is the distance from the lens to the image. The graph below shows how the image distance changes with the object distance, for two identically shaped convex lenses, A and B.
Each lens is made from a different type of glass.
[1 mark]
[2 marks]
[1 mark] (Total 12 marks) |
Follow me...
|