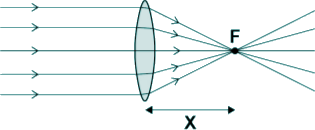
GCSE level optics questions Q22. The diagram shows parallel rays of light being refracted by a convex lens.
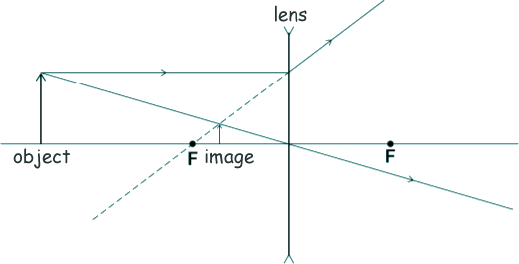
(a) What is distance ‘X’ called? Distance X is the focal length of the lens. [1 mark] (b) Lenses can be used to form the image of an object. Complete the ray diagram below to show how a convex lens forms the image of the object. Use an arrow to represent the image.
Either construct:
or
Where the constructed ray crosses the ray constructed by the examiner is the image point. An arrow perpendicular to the principal axis should be constructed as shown in the diagram. [2 marks] (c) The ray diagram below shows how a concave lens forms the image of an object.
Give one similarity and one difference between the image formed by the convex lens and the image formed by the concave lens. Similarity Both images are diminished in size (smaller than the object) Difference The concave image is virtual whereas the convex image is real or The concave image is upright but the convex image is inverted [2 marks] (d) A person uses a lens to read the letters on the back of a coin. The image height of the letters on the coin is 9.0 mm The magnification produced by the lens is 6.0 Calculate the height of the letters on the coin. Magnification = size of image/size of object 6.0 = 9.0 mm/size of object size of object = 9.0/6.0 mm [3 marks] (Total 8 marks) |
Follow me...
|