GCSE level optics questions
Q1.
The diagram shows a converging lens of focal length 4 cm being used as a magnifying glass. An object 1.6 cm tall is placed 2.4 cm from the lens.
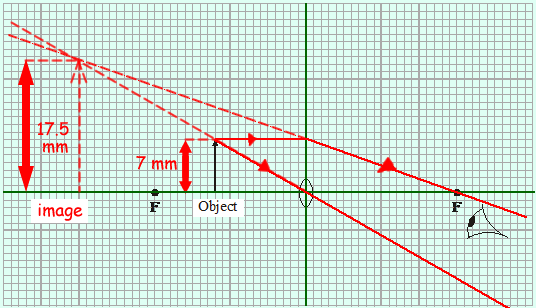
(a) On the diagram, use a ruler to construct accurately the position and size of the image. You should show how you construct your ray diagram and how light appears to come from the image to the eye.
Ray from object point through pole of the lens (centre of it!) 
Ray parallel to the principal axis going through the focal point 
Extension lines (dashed lines) for both rays meeting at a point 
Image (dashed lines) 
(4 marks)
(b) The image is virtual. What is a virtual image?
A virtual image is not real, so it cannot be picked up on a screen - the rays do not cross at the point in is formed at. Instead rays have to be traced back in a straight line to that point. 
(1 mark)
(c) Calculate the magnification produced by the lens. Show clearly how you work out your answer.
Magnification = size of image/size of object (see diagram) 
= 17.5/7 = 2.5 
(OR Magnification = image distance/object distance = u/v = 30/12 = 2.5)
(2 marks)
(Total 7 marks)


