Energy Transfer Questions - GCSE Level
Q5. A vacuum flask is designed to reduce the rate of heat transfer.
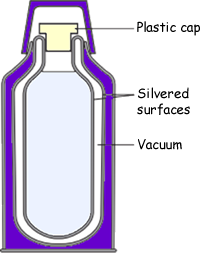
(a)
(i) Complete the table to show which methods of heat transfer are reduced by each of the features labelled in the diagram. The first row has been done for you.
(2 marks)
| Feature |
Conduction |
Convection |
Radiation |
| vacuum |
|
|
|
| silvered surfaces |
|
|
|
| plastic cap |
|
|
|
silvered surfaces - only radiation  more than the correct
number of ticks in a row
negates the mark
more than the correct
number of ticks in a row
negates the mark
plastic cap -
conduction AND convection -  both required for the mark
both required for the mark
(ii) Explain why the vacuum between the glass walls of the flask reduces heat transfer by conduction and convection. (2 marks)
Any mention of air or any other
substance in a vacuum scores
zero for this question part.
A vacuum is empty space - there are no particles atoms, molecules) in it.  Therefore heat travel methods that use particles, conduction and convection, cannot be employed.
Therefore heat travel methods that use particles, conduction and convection, cannot be employed. 
(b) The diagram shows a gas flame patio heater.
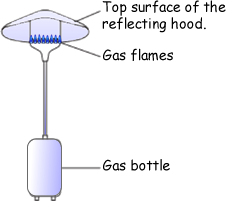
(i) Explain why the top surface of the reflecting hood should be a light, shiny surface rather than a dark, matt surface. (2 marks)
Light shiny surfaces are poor emitters of radiation  - or radiators - (OR
Dull, matt surfaces are good emitters of radiation) therefore less heat is lost
- or radiators - (OR
Dull, matt surfaces are good emitters of radiation) therefore less heat is lost  (to air above the heater)
(to air above the heater)
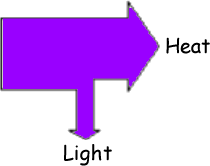
(ii) Most of the chemical energy in the gas is transformed into heat. A small amount of chemical energy is transformed into light. Draw and label a Sankey diagram for the patio heater. (2 marks)
A correct diagram must be drawn with one output arrow narrower than the other arrows.  It needs to be correctly labelled with the energy forms to get the second mark.
It needs to be correctly labelled with the energy forms to get the second mark. 
(iii) State why the total energy supplied to the patio heater must always equal the total energy transferred by the patio heater. (1 mark)
By the principle of conservation of energy, energy is neither created nor destroyed  it merely changes from one form to another.
it merely changes from one form to another.
(9 marks total)


