GCSE Questions - Hooke's Law Q4. The diagram shows a child on a playground toy.
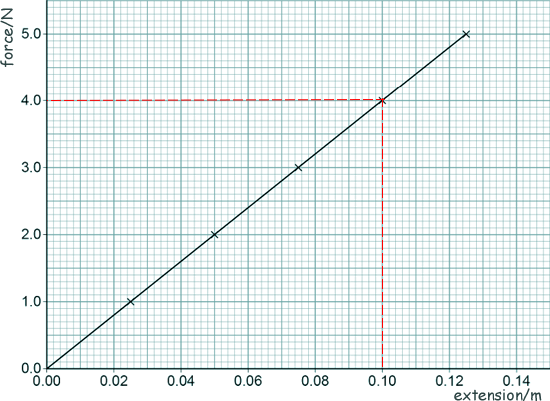
(a) The springs have been elastically deformed. Explain what is meant by 'elastically deformed'. Elastically deformed means that the speings will return to their original shape/length [2 marks] (b) Meghan investigated the relationship between the force applied to a spring and the extension of the spring. The graph below shows the results.
(a) Use the graph to determine the spring constant of the spring. Spring constant = Force/extension k = F/Δx k = 4.0/0.10
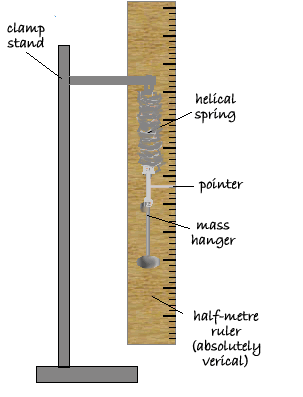
k = 40 [4 marks] (b) Meghan concluded: ‘The extension of the spring is directly proportional to the force applied to the spring.’ Explain how the graph supports the her conclusion. The line is straight [2 marks] (c) She repeated the investigation using a different spring - one with a spring constant of 13 N/m. Calculate the elastic potential energy of this spring when its extension was 20 cm. Work done in stretching the spring = area under the force extension graph Energy stored = ½FΔx F = kΔx Energy stored = ½k(Δx)2 Energy stored = ½ x 13 (0.20 Energy stored = 0.26 J [3 marks] (d) Describe a method Meghan could have used to obtain the results given in the graph above. You should include a risk assessment for one hazard in the investigation. Your answer may include a diagram.
- the examiner looks for relevant instructions - but also for the correct order - and any opposing instructions make you lose marks! It is not just a 'tick fest' - but a marker does look to see how many relevant points you have made, then considers how you have strung them together to put your answer into a 'level'
Indicative content they looked for:
[6 marks] (Total 17 marks) |
Follow me...
|