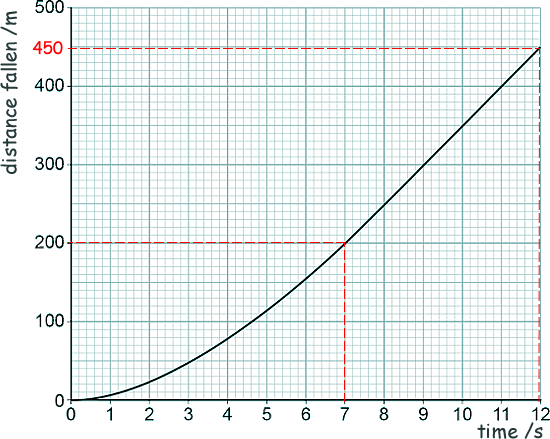
GCSE Questions: Forces Q17. An aeroplane is 4000 m above the Earth's surface. box A skydiver jumps from the aeroplane and falls vertically. The graph shows the distance the skydiver falls during the first 12 seconds after jumping.
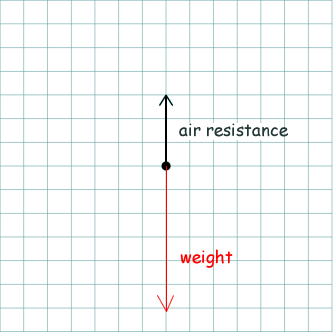
(a) The following diagram shows part of the free body diagram for the skydiver three seconds after jumping.
Complete the free body diagram for the skydiver.
[2 marks] (b) Explain the changing motion of the skydiver in terms of the forces acting on box the skydiver. Initially air resistance is less than weight/gravity, so the skydiver accelerates. The acceleration causes his velocity to increase which makes the air resistance increase. This results in the resultant force between weight and air resistance decrease. Therefore his acceleration decreases. Eventually the resultant force between weight and air resistance reduces to zero. There is then no acceleration and so the skydiver falls at terminal velocity. [4 marks] (c) Use the graph to determine the speed of the skydiver between 7 seconds and 12 seconds. In the 5 seconds he travels (450 - 200) m (see the graph) Speed = distance travelled/time taken Speed = 250/5 Speed = 50 m/s [3 marks] (d) In 2012 a skydiver jumped from a helium balloon 39,000 metres above the Earth's surface.
The skydiver reached a maximum speed of 377 m/s Jumping from 39,000 metres allowed the skydiver to reach a much higher speed than a skydiver jumping from 4000 metres. Explain why. The higher the altitude the less dense the air [3 marks] [12 Marks TOTAL] |
Follow me...
|