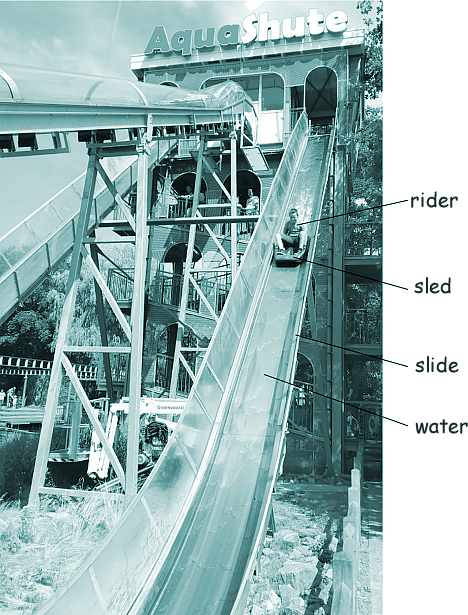
GCSE Questions: Forces Q13. The photo shows a theme park ride called AquaShute. Riders of the AquaShute sit on a sled and move down a slide.
(a) A light gate and data logger can be used to determine the speed of each rider and sled. Choose two measurements that are needed to determine the speed of a rider and sled from the box below, by 'ticking' your choices.
[2 marks] (b) The decrease in gravitational potential energy of one rider on the slide was 8.33 kJ. The rider moved through a vertical height of 17.0 m. Given that the gravitational field strength = 9.8 N/kg, calculate the mass of the rider. EGPE = mgΔh EGPE = 8.33 kJ = 8330 J 8330 = m × 9.8 × 17.0 m = 8330/(9.8 × 17.0) m m = 50.0 kg
[4 marks] (c) At the bottom of the slide, all riders and their sleds have approximately the same speed. Explain why. The kinetic energy gained at the bottom of the slide is from the loss of gravitational potential energy that was owned at the top of the slide. So decrease in EGPE = increase in EKE ½ mv2 = mgΔh Now, mass can cancel as it on both sides of the equation ½ rearranging we get: v2 = 2gh v = √(2gh) Therefore the final speed only depends on vertical height (and gravitational field strength). Variations that are observed will be due to variations in air resistance/friction or different initial speed. [4 marks] [10 Marks TOTAL] |
Follow me...
|