GCSE Questions: Energy Changes Q7. A scientist investigated how the maximum muscle power of humans varies with age and gender. The scientist asked volunteers to stand on a platform and to jump as high as they could. The diagram shows a volunteer taking part in the experiment.
An electronic timer measured the time that the volunteer was in the air.
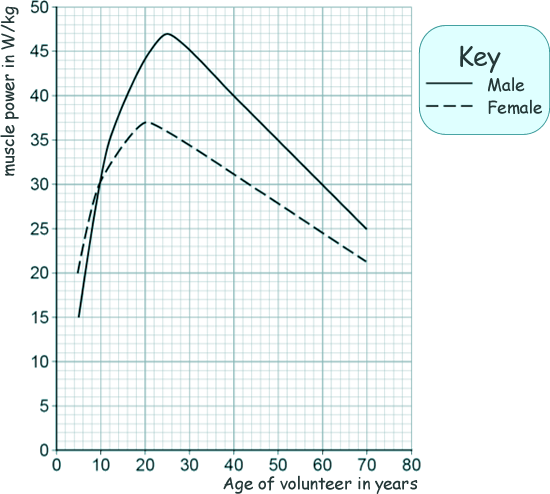
(a) The muscle power in watts per kg is calculated using the following equation: muscle power = 9.8 × jump height/time One volunteer has a muscle power of 41 W/kg. He was in the air for 0.12 s Calculate his jump height. 41 = 9.8 x h/0.12 h = 41 x 0.12/9.8 h = 0.50 m [3 marks] (b) Write down the equation which links kinetic energy, mass and speed. kinetic energy = 0.5 × mass × (speed)2 or Ek = ½ mv2 [1 mark] (c) One volunteer had a kinetic energy of 270 J and a speed of 3.0 m/s at the moment he left the ground. Calculate his mass. 270 = ½ m x 3.02 m = 270 x 2/9 m = 60 [3 marks] (d) The graph below shows the scientist's results.
Compare the muscle power of males with the muscle power of females. Use data from the graph in your answer.
- the examiner looks for relevant points - but also for a logical sequence... It is not just a 'tick fest' - but a marker does look to see how many relevant points you have made, then considers how you have strung them together to put your answer into a 'level'
Examples of physics points that should be made in the response:
[4 marks] (e) The muscle power of each volunteer was measured five times. The highest muscle power reading was recorded instead of calculating an average. Suggest one reason why. Any 1 from:
[1 mark] [Total 12 marks] |
Follow me...
|