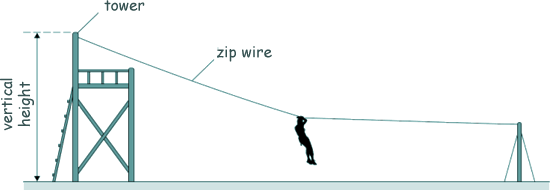
GCSE Questions: Energy Changes Q6. The diagram shows Kaylee sliding down a zip wire.
(a) Describe how the vertical height of the tower could be measured accurately. Use a tape-measure - one person holding the top of the tape and another person holding the bottom. Use a set square or a plumb-line to ensure the tape-measure is vertical. Take repeat readings, identify and omit anomalies and calculate a mean value. [2 marks] (b) When using the zip wire, Kaylee moved through a vertical height of 2.0 m Kaylee has a mass of 45 kg and the gravitational field strength = 9.8 N/kg Calculate the change in Kaylee's gravitational potential energy. Give the answer to the correct number of significant figures. ΔEGPE = mgΔh ΔEGPE = 45 x 9.8 x 2.0 ΔEGPE = 882 J ΔEGPE = 880
[4 marks] (c) As Johnny slides down the zip wire, the change in his gravitational potential energy is 1.47 kJ. His mass is 60 kg and the gravitational field strength = 9.8 N/kg Calculate the change in Johnny's vertical position. ΔEGPE = mgΔh 1.47 kJ = 1470 J 1470 = 60 x 9.8 x Δh Δh = 1470/(60 x 9.8) Δh = 2.5 m [3 marks]
(d) Give three factors that affect a person's gain in kinetic energy by the time they reach the bottom of a zip wire. Any 3 from:
[3 marks] (e) As someone moves down the zip wire their increase in kinetic energy is less than the decrease in gravitational potential energy. Explain why. Some of the gravitational energy is transferred to heat (thermal energy) that transfers to the surroundings. This is due to work done against friction with the wire and to counter air resistance.
[2 marks] (f) Different people have different speeds at the end of the zip wire. Explain why. Different people have different surface areas so would be affected by air resistance differently and result in different terminal velocities OR Their initial speed may not have been zero which would add to the total energy (of the system) OR Their masses may differ so they have different terminal velocities.
mgΔh = ½mv2 gΔh = ½v2
[2 marks maximum] [Total 16 marks] |
Follow me...
|