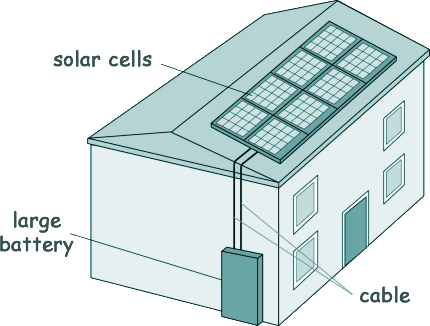
GCSE Questions: Energy Sources Q25. The diagram shows a house with a solar power system. The solar cells on the roof generate electricity for the household. When the electricity generated by the solar cells is not needed, the energy is stored in a large battery.
(a) The solar cells on the roof of the house always face in the same direction. Explain one disadvantage caused by the solar cells only facing in one direction. [2 marks] (b) The mean current from the solar cells to the battery is 3.5 A. Calculate the charge that flows from the solar cells to the battery in one hour. [3 marks] (c) At one time in the day, the total power input to the solar cells was 7500 W. Given that the efficiency of the solar cells was 0.16, calculate the useful power output of the solar cells. [4 marks] (d) The wasted energy that is not usefully transferred by the solar cells is dissipated. Choose from the phrases below what best describes what happens to energy that has been dissipated.
[1 mark] (e) Choose from the reasons below which one best describes why is it unlikely that all the UK's electricity needs could be met by solar power systems
[1 mark] (Total 11 marks) |
Follow me...
|