GCSE Questions: Energy Sources
Q3. The diagram shows how the National Grid connects power stations to consumers.
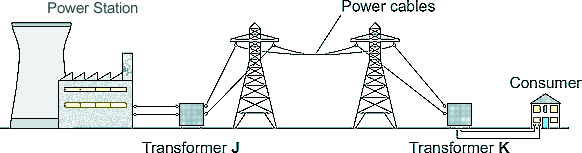
(a) Explain the role of the two transformers, J and K, in the power transmission process and the reasons for their use.
Power has two components - voltage and current. Transformer J is a step-up transformer. It raises the voltage of the electrical power output of the power station and reduces the current flowing.  Power loss from the heating of cables is dependent on current flow. Reducing current flow in a wire reduces loss of energy to the surroundings as heat energy.
Power loss from the heating of cables is dependent on current flow. Reducing current flow in a wire reduces loss of energy to the surroundings as heat energy.  High voltage transmission of power is more efficient
High voltage transmission of power is more efficient  than low voltage transmission, but it is dangerous. Therefore transformer K (a step-down transformer) reduces the voltage to a safer level
than low voltage transmission, but it is dangerous. Therefore transformer K (a step-down transformer) reduces the voltage to a safer level  as the energy gets near to the consumer.
as the energy gets near to the consumer.
[4 marks]
(b) In a pumped storage power station, water flows from a high level reservoir to a low level reservoir turning turbines and generating electricity. Pumped storage power stations do not supply electricity to the National Grid at all times of the day. The diagram belowshows a pumped storage power station.
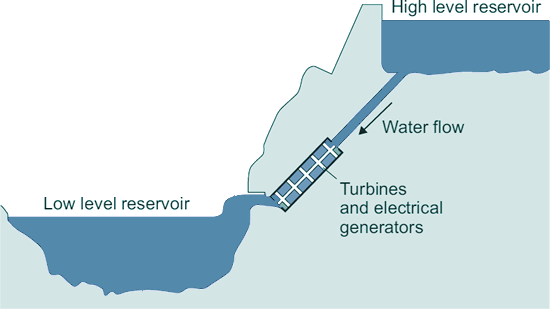
(i) Explain how pumped storage power stations store energy for later use.
At times of low demand for electricity,  when there is a surplus of electricity,
when there is a surplus of electricity,  water is pumped from low level to high level.
water is pumped from low level to high level.  Energy is then stored as gravitational potential energy.
Energy is then stored as gravitational potential energy.
[4 marks]
(ii) Explain why pumped storage power stations are able to meet sudden large demands for electricity.
Pumped storage power stations can store/produce large amount of energy by storing vast quantities of water.  That means power output can be made to increase rapidly by releasing large quantities of stored high level water.
That means power output can be made to increase rapidly by releasing large quantities of stored high level water.
[2 marks]
(Total 10 marks)


