GCSE Questions: Static Electricity Q9. When two different materials listed below are rubbed together they become electrostatically charged. The polarity of the material that is higher in the list would become positive.
(a) The diagram below shows a nylon rod being rubbed with a silk cloth.
[3 marks]
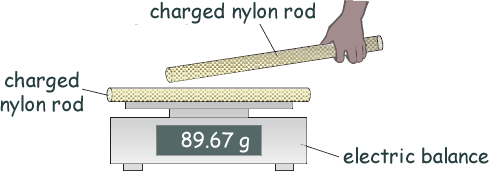
[1 mark only] (b) The charged nylon rod is put onto an electric balance.
A second identically charged nylon rod is moved towards the rod on the balance, as shown in the diagram above. Explain what will happen to the reading on the balance as the two rods get closer to each other. (The rods do not touch or discharge). Like charges repel - so as both of the rods are positively charged they repel each other.
[3 marks]
(c) A driver often becomes electrostatically charged when in a car. This happens because the driver's clothing rubs against the car seat.
[4 marks] (ii) A scientist investigated how the charge on a driver changed when the driver wore clothes made from different materials. The results from the investigation are given in the table below:
A student looked at the data and concluded: 'The charge on a driver will always be less if the driver wears clothes made from cotton rather than any other type of material.' Suggest two reasons why this may not be a valid conclusion. Not all types of material were tested - only three were tested. Other factors may affect the charge (on the driver) eg material of the seats, temperature, humidity [2 marks] [Total 13 marks]
|
Follow me...
|