GCSE Standard Questions: Electricity in the Home
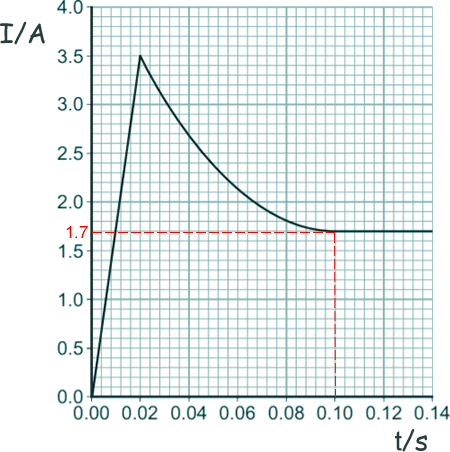
Q12. A 12 V filament bulb is connected to a 12 V power supply. The graph shows how the current changes after the bulb is switched on.
(a)
(i) After 0.10 seconds, the bulb works at its normal brightness. What is the current through the bulb when it is working at normal brightness?
1.7 A 
[1 mark]
(ii) The bulb works at normal brightness for 30 seconds before it is switched off. Calculate the charge that flows through the bulb in the 30 seconds before it is switched off.
I = Q/t
Q = It
Q = 1.7 x 30
Q = 51  C
C 
[3 marks]
(iii) Calculate the energy transferred by the 12 V bulb when it is working at normal brightness for 30 seconds.
P = IV
E/t = IV
E = ItV
E = 1.7 x 30 x 12 
E = 612  J
J 
[3 marks]
(b) Between 0.02 seconds and 0.08 seconds, there is an increase in both the resistance and the temperature of the metal filament inside the bulb.
Explain, in terms of the electrons and ions inside the filament, why both the temperature and the resistance increase.
As the current passes though the filament the ions in the metal lattice vibrate faster and/or with a bigger amplitude.  This means that the temperature of the metal increases. This means that the 'free' electrons collide more (frequently) with the ions making the drift velocity of electrons decrease,
This means that the temperature of the metal increases. This means that the 'free' electrons collide more (frequently) with the ions making the drift velocity of electrons decrease,  indicating an increase in the resistance of the metal filament..
indicating an increase in the resistance of the metal filament..
[2 marks]
(Total 10 marks)







