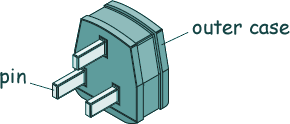
GCSE Standard Questions: Electricity in the Home Q11. A washing machine is connected to the mains electricity supply using a cable and three-pin plug. (a) Here is a three-pin plug.
[1 mark]
[1 mark]
(b) The three-pin plug contains a fuse. The fuse is connected to one of the wires inside the cable.
[1 mark]
[1 mark]
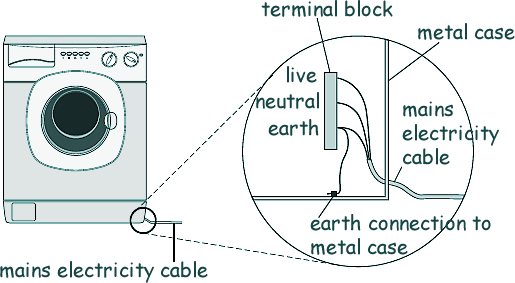
[4 marks] (c) The diagram below shows how the mains electricity cable is connected to the washing machine. The earth wire is connected to the metal case of the washing machine.
If a fault makes the metal case live, the earth wire and fuse inside the plug prevent the mains cable from overheating and causing a fire. Explain how. The earth wire is at 0V. The live wire (and therefore the metal cas) is varying from a maximum of 330V to -330V fifty times a second. As soon as the earthed case becomes live, a large current flows through the live wire to earth
[2 marks] (d) New research has shown that many people underestimate the hazards of using mains electricity. It is important that people do understand the hazards of using mains electricity. Suggest why. To reduce the chance of people getting an electric shock /electrocuted/being killed OR to reduce the risk of an accident/ (electrical) fire. [1 mark] (Total 11 marks) |
Follow me...
|