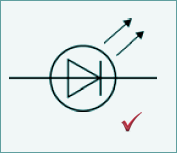
GCSE Standard Questions: Electricity in the Home Q10. The lighting in a home may be provided by LED bulbs, filament bulbs or halogen bulbs. (a)
[1 mark]
[6 marks] (b) The resistance of a filament bulb increases as the temperature of the filament increases. Explain, in terms of the electrons and ions inside the filament, why the resistance increases. As the temperature increases the ions in the metal lattice of the filament gain energy and vibrate faster (and/or with a bigger amplitude)
The electrons collide more frequently with the ions this makes the 'drift velocity' of the electrons decrease.
[2 marks] (c) Why are LED bulbs cheaper to use than filament bulbs or halogen bulbs that produce Any one from:
[1 mark] (Total 10 marks) |
Follow me...
|